Page 847 - Read Online
P. 847
Page 4 of 17 Melillo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:81 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.83
A B
C
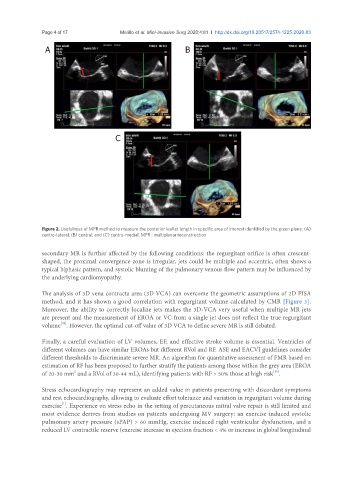
Figure 2. Usefulness of MPR method to measure the posterior leaflet length in specific area of interest identified by the green plane: (A)
centro-lateral; (B) central; and (C) centro-medial. MPR : multiplanar reconstruction
secondary MR is further affected by the following conditions: the regurgitant orifice is often crescent-
shaped, the proximal convergence zone is irregular, jets could be multiple and eccentric, often shows a
typical biphasic pattern, and systolic blunting of the pulmonary venous flow pattern may be influenced by
the underlying cardiomyopathy.
The analysis of 3D vena contracta area (3D VCA) can overcome the geometric assumptions of 2D PISA
method, and it has shown a good correlation with regurgitant volume calculated by CMR [Figure 3].
Moreover, the ability to correctly localize jets makes the 3D-VCA very useful when multiple MR jets
are present and the measurement of EROA or VC from a single jet does not reflect the true regurgitant
volume . However, the optimal cut-off value of 3D VCA to define severe MR is still debated.
[10]
Finally, a careful evaluation of LV volumes, EF, and effective stroke volume is essential. Ventricles of
different volumes can have similar EROAs but different RVol and RF. ASE and EACVI guidelines consider
different thresholds to discriminate severe MR. An algorithm for quantitative assessment of FMR based on
estimation of RF has been proposed to further stratify the patients among those within the grey area (EROA
2
[11]
of 20-30 mm and a RVol of 30-44 mL), identifying patients with RF > 50% those at high risk .
Stress echocardiography may represent an added value in patients presenting with discordant symptoms
and rest echocardiography, allowing to evaluate effort tolerance and variation in regurgitant volume during
[1]
exercise . Experience on stress echo in the setting of percutaneous mitral valve repair is still limited and
most evidence derives from studies on patients undergoing MV surgery: an exercise induced systolic
pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) > 60 mmHg, exercise induced right ventricular dysfunction, and a
reduced LV contractile reserve (exercise increase in ejection fraction < 4% or increase in global longitudinal