Page 93 - Read Online
P. 93
Chiu Modified parasternal approach for aortic valve surgery
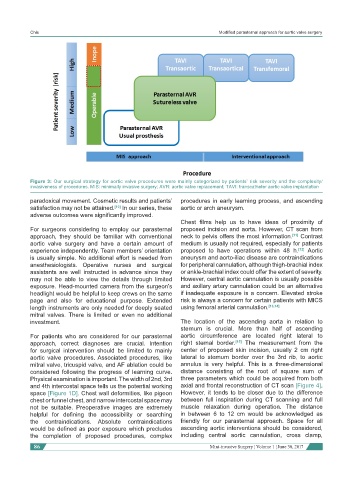
Figure 3: Our surgical strategy for aortic valve procedures were mainly categorized by patients’ risk severity and the complexity/
invasiveness of procedures. MIS: minimally invasive surgery; AVR: aortic valve replacement; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
paradoxical movement. Cosmetic results and patients’ procedures in early learning process, and ascending
satisfaction may not be attained. [10] In our series, these aortic or arch aneurysm.
adverse outcomes were significantly improved.
Chest films help us to have ideas of proximity of
For surgeons considering to employ our parasternal proposed incision and aorta. However, CT scan from
approach, they should be familiar with conventional neck to pelvis offers the most information. Contrast
[11]
aortic valve surgery and have a certain amount of medium is usually not required, especially for patients
experience independently. Team members’ orientation proposed to have operations within 48 h. [12] Aortic
is usually simple. No additional effort is needed from aneurysm and aorto-iliac disease are contraindications
anesthesiologists. Operative nurses and surgical for peripheral cannulation, although thigh-brachial index
assistants are well instructed in advance since they or ankle-brachial index could offer the extent of severity.
may not be able to view the details through limited However, central aortic cannulation is usually possible
exposure. Head-mounted camera from the surgeon’s and axillary artery cannulation could be an alternative
headlight would be helpful to keep crews on the same if inadequate exposure is a concern. Elevated stroke
page and also for educational purpose. Extended risk is always a concern for certain patients with MICS
length instruments are only needed for deeply seated using femoral arterial cannulation. [13,14]
mitral valves. There is limited or even no additional
investment. The location of the ascending aorta in relation to
sternum is crucial. More than half of ascending
For patients who are considered for our parasternal aortic circumference are located right lateral to
approach, correct diagnoses are crucial. Intention right sternal border. [15] The measurement from the
for surgical intervention should be limited to mainly center of proposed skin incision, usually 2 cm right
aortic valve procedures. Associated procedures, like lateral to sternum border over the 3rd rib, to aortic
mitral valve, tricuspid valve, and AF ablation could be annulus is very helpful. This is a three-dimensional
considered following the progress of learning curve. distance consisting of the root of square sum of
Physical examination is important. The width of 2nd, 3rd three parameters which could be acquired from both
and 4th intercostal space tells us the potential working axial and frontal reconstruction of CT scan [Figure 4].
space [Figure 1D]. Chest wall deformities, like pigeon However, it tends to be closer due to the difference
chest or funnel chest, and narrow intercostal space may between full inspiration during CT scanning and full
not be suitable. Preoperative images are extremely muscle relaxation during operation. The distance
helpful for defining the accessibility or searching in between 6 to 12 cm would be acknowledged as
the contraindications. Absolute contraindications friendly for our parasternal approach. Space for all
would be defined as poor exposure which precludes ascending aortic interventions should be considered,
the completion of proposed procedures, complex including central aortic cannulation, cross clamp,
86 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017