Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
Chiu Modified parasternal approach for aortic valve surgery
one-rib parasternal approach. All surgical details were management consisted of controlled local anesthetic
similar, except for a smaller incision and only the 3rd infusion and a patient-controlled analgesia pump.
rib was cut. A one-rib approach was usually aimed for
an isolated aortic procedure. The major determinant RESULTS
for this approach would be the length between the
lower margin of 2nd rib and upper margin of 4th rib. From 2004 to 2016, 543 parasternal cardiac operations
For patients with a narrow 2nd intercostal space, this were performed at our institution. The cases
would be difficult to proceed [Figure 1D]. For more than included 297 isolated aortic valve, 124 aortic and
two thirds of these patients, central aortic cannulation mitral, 45 aortic, mitral and tricuspid procedures and
could be achieved. Some patients had concomitant miscellaneous applications. Nine percent were redo
mitral repair as well. We also developed epicardialcryo- procedures. Average time for parasternal cross clamp,
ablation for AF using pulmonary vein isolation through CPB, operation were 61.84, 101.43 and 243.00 min,
this limited incision. respectively [Table 1]. Average ventilation time and
intensive care unit stay were 13 h and 2.4 days [Table 2].
After the completion of valvular procedures, CPB Surgical mortality was 1.9%. There was one conversion
was weaned off and hemostasis was achieved. Two to sternotomy for persistent bleeding. Five patients
Jackson-Pratt drains were inserted into pericardial and had perioperative central nervous complications.
pleural space, respectively. Pericardium was closed Retrograde flow from femoral cannulation and
with interrupted sutures. The myocostal flap was inadequate de-airing were considered to be potential
reduced back into the anatomical position. Any partially causes. Parasternal wound complications were rare
broken ribs was fixed with a pediatric wire to sternum. and self-limited. The well vascularized pectoralis
For patients with widened 2nd intercostal space, muscle coverage potentially decreased local infection.
several interrupted, braided, non-absorbable sutures Eight patients had a wound infection that required
were used as a fence to divide the space and prevent additional limited surgical debridement without the
lung herniation. Mesh for abdominal hernia and ePTFE entry of mediastinum. Three of them had local infection
patch had been placed in selective cases. The pectoral related to temporary pacemaker wires [Table 3]. Pain
major muscle was brought back centrally and fixed analogue scale was usually less than 2-3 under our
with interrupted sutures. Subcutaneous fascia and aggressive pain management. More than 90% patients
skin were closed [Figure 2B-D]. Our postoperative pain were satisfied with their operative wounds.
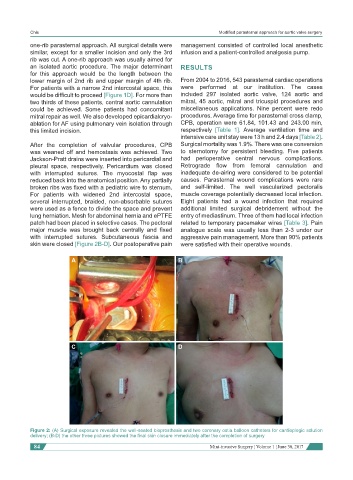
A B
C D
Figure 2: (A) Surgical exposure revealed the well-seated bioprosthesis and two coronary ostia balloon catheters for cardioplegic solution
delivery; (B-D) the other three pictures showed the final skin closure immediately after the completion of surgery
84 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017