Page 189 - Read Online
P. 189
Jairath et al. Percutaneous nephrostomy
A B
C D
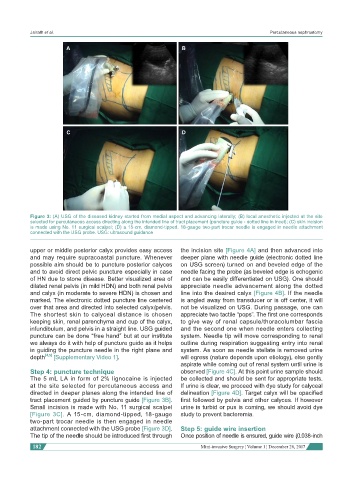
Figure 3: (A) USG of the diseased kidney started from medial aspect and advancing laterally; (B) local anesthetic injected at the site
selected for percutaneous access directing along the intended line of tract placement (puncture guide - dotted line in incet); (C) skin incision
is made using No. 11 surgical scalpel; (D) a 15-cm, diamond-tipped, 18-gauge two-part trocar needle is engaged in needle attachment
connected with the USG probe. USG: ultrasound guidance
upper or middle posterior calyx provides easy access the incision site [Figure 4A] and then advanced into
and may require supracoastal puncture. Whenever deeper plane with needle guide (electronic dotted line
possible aim should be to puncture posterior calyces on USG screen) turned on and beveled edge of the
and to avoid direct pelvic puncture especially in case needle facing the probe (as beveled edge is echogenic
of HN due to stone disease. Better visualized area of and can be easily differentiated on USG). One should
dilated renal pelvis (in mild HDN) and both renal pelvis appreciate needle advancement along the dotted
and calyx (in moderate to severe HDN) is chosen and line into the desired calyx [Figure 4B]. If the needle
marked. The electronic dotted puncture line centered is angled away from transducer or is off center, it will
over that area and directed into selected calyx/pelvis. not be visualized on USG. During passage, one can
The shortest skin to calyceal distance is chosen appreciate two tactile “pops”. The first one corresponds
keeping skin, renal parenchyma and cup of the calyx, to give way of renal capsule/thoracolumbar fascia
infundibulum, and pelvis in a straight line. USG guided and the second one when needle enters collecting
puncture can be done “free hand” but at our institute system. Needle tip will move corresponding to renal
we always do it with help of puncture guide as it helps outline during respiration suggesting entry into renal
in guiding the puncture needle in the right plane and system. As soon as needle stellate is removed urine
depth [4,5] [Supplementary Video 1]. will egress (nature depends upon etiology), else gently
aspirate while coming out of renal system until urine is
Step 4: puncture technique observed [Figure 4C]. At this point urine sample should
The 5 mL LA in form of 2% lignocaine is injected be collected and should be sent for appropriate tests.
at the site selected for percutaneous access and If urine is clear, we proceed with dye study for calyceal
directed in deeper planes along the intended line of delineation [Figure 4D]. Target calyx will be opacified
tract placement guided by puncture guide [Figure 3B]. first followed by pelvis and other calyces. If however
Small incision is made with No. 11 surgical scalpel urine is turbid or pus is coming, we should avoid dye
[Figure 3C]. A 15-cm, diamond-tipped, 18-gauge study to prevent bacteremia.
two-part trocar needle is then engaged in needle
attachment connected with the USG probe [Figure 3D]. Step 5: guide wire insertion
The tip of the needle should be introduced first through Once position of needle is ensured, guide wire (0.038-inch
182 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017