Page 190 - Read Online
P. 190
Jairath et al. Percutaneous nephrostomy
A B
C D
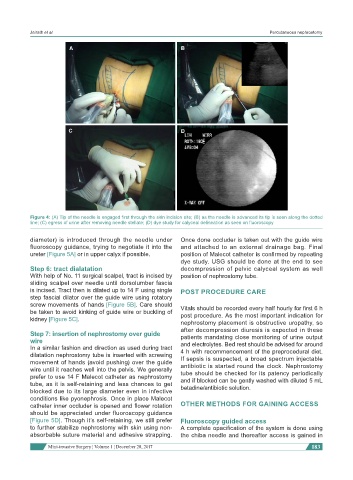
Figure 4: (A) Tip of the needle is engaged first through the skin incision site; (B) as the needle is advanced its tip is seen along the dotted
line; (C) egress of urine after removing needle stellate; (D) dye study for calyceal delineation as seen on fluoroscopy
diameter) is introduced through the needle under Once done occluder is taken out with the guide wire
fluoroscopy guidance, trying to negotiate it into the and attached to an external drainage bag. Final
ureter [Figure 5A] or in upper calyx if possible. position of Malecot catheter is confirmed by repeating
dye study. USG should be done at the end to see
Step 6: tract dialatation decompression of pelvic calyceal system as well
With help of No. 11 surgical scalpel, tract is incised by position of nephrostomy tube.
sliding scalpel over needle until dorsolumber fascia
is incised. Tract then is dilated up to 14 F using single POST PROCEDURE CARE
step fascial dilator over the guide wire using rotatory
screw movements of hands [Figure 5B]. Care should Vitals should be recorded every half hourly for first 6 h
be taken to avoid kinking of guide wire or buckling of post procedure. As the most important indication for
kidney [Figure 5C].
nephrostomy placement is obstructive uropathy, so
after decompression diuresis is expected in these
Step 7: insertion of nephrostomy over guide patients mandating close monitoring of urine output
wire and electrolytes. Bed rest should be advised for around
In a similar fashion and direction as used during tract 4 h with recommencement of the preprocedural diet.
dilatation nephrostomy tube is inserted with screwing If sepsis is suspected, a broad spectrum injectable
movement of hands (avoid pushing) over the guide antibiotic is started round the clock. Nephrostomy
wire until it reaches well into the pelvis. We generally
prefer to use 14 F Malecot catheter as nephrostomy tube should be checked for its patency periodically
and if blocked can be gently washed with diluted 5 mL
tube, as it is self-retaining and less chances to get betadine/antibiotic solution.
blocked due to its large diameter even in infective
conditions like pyonephrosis. Once in place Malecot
catheter inner occluder is opened and flower rotation OTHER METHODS FOR GAINING ACCESS
should be appreciated under fluoroscopy guidance
[Figure 5D]. Though it’s self-retaining, we still prefer Fluoroscopy guided access
to further stabilize nephrostomy with skin using non- A complete opacification of the system is done using
absorbable suture material and adhesive strapping. the chiba needle and thereafter access is gained in
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 183