Page 191 - Read Online
P. 191
Jairath et al. Percutaneous nephrostomy
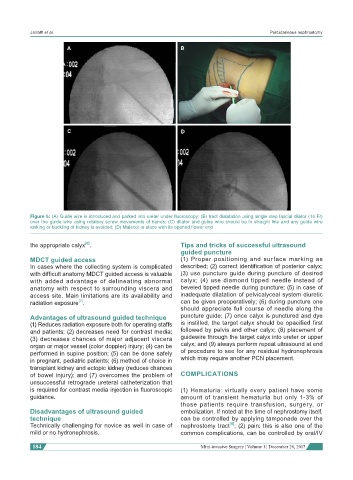
A B
C D
Figure 5: (A) Guide wire is introduced and parked into ureter under fluoroscopy; (B) tract dialatation using single step fascial dilator (14 Fr)
over the guide wire using rotatory screw movements of hands; (C) dilator and guide wire should be in straight line and any guide wire
kinking or buckling of kidney is avoided; (D) Malecot in place with its opened flower end
[6]
the appropriate calyx . Tips and tricks of successful ultrasound
guided puncture
MDCT guided access (1) Proper positioning and surface marking as
In cases where the collecting system is complicated described; (2) correct identification of posterior calyx;
with difficult anatomy MDCT guided access is valuable (3) use puncture guide during puncture of desired
with added advantage of delineating abnormal calyx; (4) use diamond tipped needle instead of
anatomy with respect to surrounding viscera and beveled tipped needle during puncture; (5) in case of
access site. Main limitations are its availability and inadequate dilatation of pelvicalyceal system diuretic
[7]
radiation exposure . can be given preoperatively; (6) during puncture one
should appreciate full course of needle along the
Advantages of ultrasound guided technique puncture guide; (7) once calyx is punctured and dye
(1) Reduces radiation exposure both for operating staffs is instilled, the target calyx should be opacified first
and patients; (2) decreases need for contrast media; followed by pelvis and other calyx; (8) placement of
(3) decreases chances of major adjacent viscera guidewire through the target calyx into ureter or upper
organ or major vessel (color doppler) injury; (4) can be calyx; and (9) always perform repeat ultrasound at end
performed in supine position; (5) can be done safely of procedure to see for any residual hydronephrosis
in pregnant, pediatric patients; (6) method of choice in which may require another PCN placement.
transplant kidney and ectopic kidney (reduces chances
of bowel injury); and (7) overcomes the problem of COMPLICATIONS
unsuccessful retrograde ureteral catheterization that
is required for contrast media injection in fluoroscopic (1) Hematuria: virtually every patient have some
guidance. amount of transient hematuria but only 1-3% of
those patients require transfusion, surgery, or
Disadvantages of ultrasound guided embolization. If noted at the time of nephrostomy itself,
technique can be controlled by applying tamponade over the
[8]
Technically challenging for novice as well in case of nephrostomy tract ; (2) pain: this is also one of the
mild or no hydronephrosis. common complications, can be controlled by oral/IV
184 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017