Page 184 - Read Online
P. 184
Yuu et al. Laparoscopic surgery for psychotic
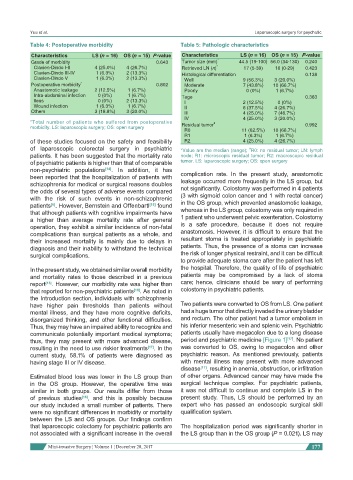
Table 4: Postoperative morbidity Table 5: Pathologic characteristics
Characteristics LS (n = 16) OS (n = 15) P-value Characteristics LS (n = 16) OS (n = 15) P-value
Grade of morbidity 0.643 Tumor size (mm) * 44.5 (19-100) 56.0 (34-130) 0.240
Clavien-Dindo I-II 4 (25.0%) 4 (26.7%) Retrieved LN (n) * 17 (5-39) 16 (0-29) 0.423
Clavien-Dindo III-IV 1 (6.3%) 2 (13.3%) Histological differentiation 0.138
Clavien-Dindo V 1 (6.3%) 2 (13.3%) Well 9 (56.3%) 3 (20.0%)
Postoperative morbidity * 0.802 Moderate 7 (43.8%) 10 (66.7%)
Anastomotic leakage 2 (12.5%) 1 (6.7%) Poorly 0 (0%) 1 (6.7%)
Intra-abdominal infection 0 (0%) 1 (6.7%) Tage 0.363
Ileus 0 (0%) 2 (13.3%) I 2 (12.5%) 0 (0%)
Wound infection 1 (6.3%) 1 (6.7%) II 6 (37.5%) 4 (26.7%)
Others 3 (18.8%) 3 (20.0%) III 4 (25.0%) 7 (46.7%)
IV 4 (25.0%) 3 (20.0%)
*Total number of patients who suffered from postoperative Residual tumor # 0.992
morbidity. LS: laparoscopic surgery; OS: open surgery
R0 11 (62.5%) 10 (66.7%)
R1 1 (6.3%) 1 (6.7%)
of these studies focused on the safety and feasibility R2 4 (25.0%) 4 (26.7%)
of laparoscopic colorectal surgery in psychiatric *Value are the median (range); R0: no residual tumor; LN: lymph
#
patients. It has been suggested that the mortality rate node; R1: microscopic residual tumor; R2: macroscopic residual
of psychiatric patients is higher than that of comparable tumor. LS: laparoscopic surgery; OS: open surgery
non-psychiatric populations [14] . In addition, it has
been reported that the hospitalization of patients with complication rate. In the present study, anastomotic
schizophrenia for medical or surgical reasons doubles leakage occurred more frequently in the LS group, but
the odds of several types of adverse events compared not significantly. Colostomy was performed in 4 patients
with the risk of such events in non-schizophrenic (3 with sigmoid colon cancer and 1 with rectal cancer)
patients . However, Bernstein and Offenbartl [15] found in the OS group, which prevented anastomotic leakage,
[6]
that although patients with cognitive impairments have whereas in the LS group, colostomy was only required in
a higher than average mortality rate after general 1 patient who underwent pelvic exenteration. Colostomy
operation, they exhibit a similar incidence of non-fatal is a safe procedure, because it does not require
complications than surgical patients as a whole, and anastomosis. However, it is difficult to ensure that the
their increased mortality is mainly due to delays in resultant stoma is treated appropriately in psychiatric
diagnosis and their inability to withstand the technical patients. Thus, the presence of a stoma can increase
surgical complications. the risk of longer physical restraint, and it can be difficult
to provide adequate stoma care after the patient has left
In the present study, we obtained similar overall morbidity the hospital. Therefore, the quality of life of psychiatric
and mortality rates to those described in a previous patients may be compromised by a lack of stoma
report [13] . However, our morbidity rate was higher than care; hence, clinicians should be wary of performing
that reported for non-psychiatric patients [16] . As noted in colostomy in psychiatric patients.
the Introduction section, individuals with schizophrenia
have higher pain thresholds than patients without Two patients were converted to OS from LS. One patient
mental illness, and they have more cognitive deficits, had a huge tumor that directly invaded the urinary bladder
disorganized thinking, and other functional difficulties. and rectum. The other patient had a tumor embolism in
Thus, they may have an impaired ability to recognize and his inferior mesenteric vein and splenic vein. Psychiatric
communicate potentially important medical symptoms; patients usually have megacolon due to a long disease
thus, they may present with more advanced disease, period and psychiatric medicine [Figure 1] [17] . No patient
resulting in the need to use riskier treatments [17] . In the was converted to OS, owing to megacolon and other
current study, 58.1% of patients were diagnosed as psychiatric reason. As mentioned previously, patients
having stage III or IV disease. with mental illness may present with more advanced
disease [17] , resulting in anemia, obstruction, or infiltration
Estimated blood loss was lower in the LS group than of other organs. Advanced cancer may have made the
in the OS group. However, the operative time was surgical technique complex. For psychiatric patients,
similar in both groups. Our results differ from those it was not difficult to continue and complete LS in the
of previous studies [16] , and this is possibly because present study. Thus, LS should be performed by an
our study included a small number of patients. There expert who has passed an endoscopic surgical skill
were no significant differences in morbidity or mortality qualification system.
between the LS and OS groups. Our findings confirm
that laparoscopic colectomy for psychiatric patients are The hospitalization period was significantly shorter in
not associated with a significant increase in the overall the LS group than in the OS group (P = 0.021). LS may
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 177