Page 182 - Read Online
P. 182
Yuu et al. Laparoscopic surgery for psychotic
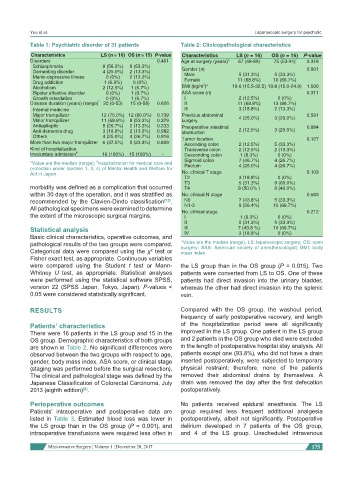
Table 1: Psychiatric disorder of 31 patients Table 2: Clinicopathological characteristics
Characteristics LS (n = 16) OS (n = 15) P-value Characteristics LS (n = 16) OS (n = 15) P-value
Disorders 0.461 Age at surgery (years)* 67 (48-89) 75 (53-91) 0.318
Schizophrenia 9 (56.3%) 8 (53.3%)
Dementing disorder 4 (25.0%) 2 (13.3%) Gender (n) 0.901
Manic-depressive illness 0 (0%) 2 (13.3%) Male 5 (31.3%) 5 (33.3%)
Drug addiction 1 (6.3%) 0 (0%) Female 2 11 (68.8%) 10 (66.7%)
Alcoholism 2 (12.5%) 1 (6.7%) BMI (kg/m )* 19.6 (15.5-32.5) 19.8 (15.0-24.9) 1.000
Bipolar affective disorder 0 (0%) 1 (6.7%) ASA score (n) 0.311
Growth retardation 0 (0%) 1 (6.7%) I 2 (12.5%) 0 (0%)
Disease duration (years) (range) * 20 (0-53) 15 (0-58) 0.626 II 11 (68.8%) 13 (86.7%)
Internal medicine III 3 (18.8%) 2 (13.3%)
Major tranquilizer 12 (75.0%) 12 (80.0%) 0.739 Previous abdominal 0.561
Minor tranquilizer 11 (68.8%) 8 (53.3%) 0.379 surgery 4 (25.0%) 3 (20.0%)
Antiepileptic 5 (26.7%) 2 (13.3%) 0.233 Preoperative intestinal 0.884
Anti-dementia drug 3 (18.8%) 2 (13.3%) 0.982 obstruction 2 (12.5%) 3 (20.0%)
Others 4 (25.0%) 4 (26.7%) 0.916 Tumor location 0.127
More than two major tranquilizer 6 (37.5%) 5 (23.3%) 0.809 Ascending colon 2 (12.5%) 5 (33.3%)
Kind of hospitalization Transverse colon 2 (12.5%) 2 (13.3%)
Involuntary admission # 16 (100%) 15 (100%) - Descending colon 1 (6.3%) 0 (0%)
#
*Value are the median (range); hospitalization for medical care and Sigmoid colon 7 (46.7%) 4 (26.7%)
4 (26.7%)
4 (25.0%)
Rectum
protection under (section 1, 3, 4) of Mental Health and Welfare for
Act in Japan No. clinical T stage 0.103
T2 3 (18.8%) 0 (0%)
T3 5 (31.3%) 9 (60.0%)
morbidity was defined as a complication that occurred T4 8 (50.0% ) 6 (40.0%)
within 30 days of the operation, and it was stratified as No. clinical N stage 0.563
recommended by the Clavien-Dindo classification [12] . N0 7 (43.8%) 5 (33.3%)
All pathological specimens were examined to determine N1-3 9 (56.4%) 10 (66.7%)
the extent of the microscopic surgical margins. No. clinical stage 1 (6.3%) 0 (0%) 0.212
I
II 5 (31.3%) 5 (33.3%)
Statistical analysis III 7 (43.8 %) 10 (66.7%)
Basic clinical characteristics, operative outcomes, and IV 3 (18.8%) 0 (0%)
pathological results of the two groups were compared. *Value are the median (range). LS: laparoscopic surgery; OS: open
Categorical data were compared using the χ test or surgery; ASA: American society of anesthesiologist; BMI: body
2
mass index
Fisher exact test, as appropriate. Continuous variables
were compared using the Student t test or Mann- the LS group than in the OS group (P = 0.015). Two
Whitney U test, as appropriate. Statistical analyses patients were converted from LS to OS. One of these
were performed using the statistical software SPSS, patients had direct invasion into the urinary bladder,
version 22 (SPSS Japan, Tokyo, Japan). P-values < whereas the other had direct invasion into the splenic
0.05 were considered statistically significant. vein.
RESULTS Compared with the OS group, the washout period,
frequency of early postoperative recovery, and length
Patients’ characteristics of the hospitalization period were all significantly
There were 16 patients in the LS group and 15 in the improved in the LS group. One patient in the LS group
OS group. Demographic characteristics of both groups and 2 patients in the OS group who died were excluded
are shown in Table 2. No significant differences were in the length of postoperative hospital stay analysis. All
observed between the two groups with respect to age, patients except one (93.8%), who did not have a drain
gender, body mass index, ASA score, or clinical stage inserted postoperatively, were subjected to temporary
(staging was performed before the surgical resection). physical restraint; therefore, none of the patients
The clinical and pathological stage was defined by the removed their abdominal drains by themselves. A
Japanese Classification of Colorectal Carcinoma, July drain was removed the day after the first defecation
2013 (eighth edition) . postoperatively.
[9]
Perioperative outcomes No patients received epidural anesthesia. The LS
Patients’ intraoperative and postoperative data are group required less frequent additional analgesia
listed in Table 3. Estimated blood loss was lower in postoperatively, albeit not significantly. Postoperative
the LS group than in the OS group (P = 0.001), and delirium developed in 7 patients of the OS group,
intraoperative transfusions were required less often in and 4 of the LS group. Unscheduled intravenous
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 175