Page 177 - Read Online
P. 177
De Aquino et al. Esophageal mucosectomy in advanced achalasia
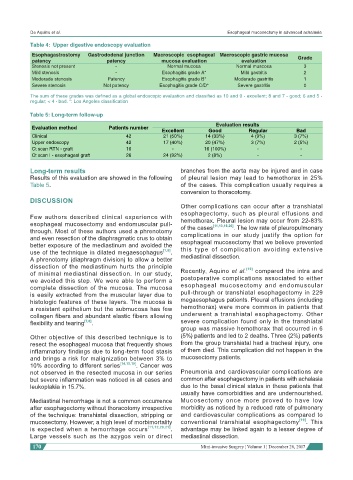
Table 4: Upper digestive endoscopy evaluation
Esophagastrostomy Gastrododenal junction Macroscopic esophageal Macroscopic gastric mucosa Grade
patency patency mucosa evaluation evaluation
Stenosis not present - Normal mucosa Normal muscosa 3
Mild stenosis - Esophagitis grade A* Mild gastritis 2
Moderade stenosis Patency Esophagitis grade B* Moderade gastritis 1
Severe stenosis Not patency Esophagitis grade C/D* Severe gastritis 0
The sum of these grades was defined as a global endoscopic evaluation and classified as 10 and 9 - excellent; 8 and 7 - good; 6 and 5 -
regular; < 4 - bad. *: Los Angeles classification
Table 5: Long-term follow-up
Evaluation results
Evaluation method Patients number
Excellent Good Regular Bad
Clinical 42 21 (50%) 14 (33%) 4 (9%) 3 (7%)
Upper endoscopy 42 17 (40%) 20 (47%) 3 (7%) 2 (5%)
Ct scan RTN - graft 16 - 16 (100%) - -
Ct scan I - esophageal graft 26 24 (92%) 2 (8%) - -
Long-term results branches from the aorta may be injured and in case
Results of this evaluation are showed in the following of pleural lesion may lead to hemothorax in 25%
Table 5. of the cases. This complication usually requires a
conversion to thoracotomy.
DISCUSSION
Other complications can occur after a transhiatal
esophagectomy, such as pleural effusions and
Few authors described clinical experience with hemothorax. Pleural lesion may occur from 22-83%
esophageal mucosectomy and endomuscular pull- of the cases [11,13,18,20] . The low rate of pleuropulmonary
through. Most of these authors used a phrenotomy
and even resection of the diaphragmatic crus to obtain complications in our study justify the option for
better exposure of the mediastinum and avoided the esophageal mucosectomy that we believe prevented
use of the technique in dilated megaesophagus [7,8] . this type of complication avoiding extensive
A phrenotomy (diaphragm division) to allow a better mediastinal dissection.
dissection of the mediastinum hurts the principle [19]
of minimal mediastinal dissection. In our study, Recently, Aquino et al. compared the intra and
we avoided this step. We were able to perform a postoperative complications associated to either
complete dissection of the mucosa. The mucosa esophageal mucosectomy and endomuscular
is easily extracted from the muscular layer due to pull-through or transhiatal esophagectomy in 229
histologic features of these layers. The mucosa is megaesophagus patients. Pleural effusions (including
a resistant epithelium but the submucosa has few hemothorax) were more common in patients that
collagen fibers and abundant elastic fibers allowing underwent a transhiatal esophagectomy. Other
flexibility and tearing [7,8] . severe complication found only in the transhiatal
group was massive hemothorax that occurred in 6
Other objective of this described technique is to (5%) patients and led to 2 deaths. Three (2%) patients
resect the esophageal mucosa that frequently shows from the group transhiatal had a tracheal injury, one
inflammatory findings due to long-term food stasis of them died. This complication did not happen in the
and brings a risk for malignization between 3% to mucosectomy patients.
10% according to different series [14,15,19] . Cancer was
not observed in the resected mucosa in our series Pneumonia and cardiovascular complications are
but severe inflammation was noticed in all cases and common after esophagectomy in patients with achalasia
leukoplakia in 15.7%. due to the basal clinical status in these patients that
usually have comorbidities and are undernourished.
Mediastinal hemorrhage is not a common occurrence Mucosectomy once more proved to have low
after esophagectomy without thoracotomy irrespective morbidity as noticed by a reduced rate of pulmonary
of the technique: transhiatal dissection, stripping or and cardiovascular complications as compared to
mucosectomy. However, a high level of morbimortality conventional transhiatal esophagectomy [19] . This
is expected when a hemorrhage occurs [11,12,20,21] . advantage may be linked again to a lesser degree of
Large vessels such as the azygos vein or direct mediastinal dissection.
170 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017