Page 150 - Read Online
P. 150
Agrawal et al. Challenging treatment of huge fibromatosis
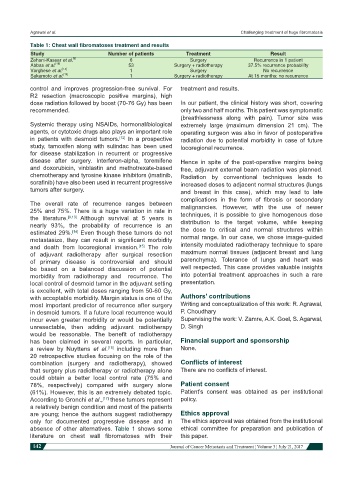
Table 1: Chest wall fibromatoses treatment and results
Study Number of patients Treatment Result
Zehani-Kassar et al. [8] 6 Surgery Recurrence in 1 patient
Abbas et al. [18] 53 Surgery + radiotherapy 37.5% recurrence probability
Varghese et al. [14] 1 Surgery No recurrence
Sakamoto et al. [19] 1 Surgery + radiotherapy At 15 months: no recurrence
control and improves progression-free survival. For treatment and results.
R2 resection (macroscopic positive margins), high
dose radiation followed by boost (70-76 Gy) has been In our patient, the clinical history was short, covering
recommended. only two and half months. This patient was symptomatic
(breathlessness along with pain). Tumor size was
Systemic therapy using NSAIDs, hormonal/biological extremely large (maximum dimension 21 cm). The
agents, or cytotoxic drugs also plays an important role operating surgeon was also in favor of postoperative
in patients with desmoid tumors. In a prospective radiation due to potential morbidity in case of future
[12]
study, tamoxifen along with sulindac has been used locoregional recurrence.
for disease stabilization in recurrent or progressive
disease after surgery. Interferon-alpha, toremifene Hence in spite of the post-operative margins being
and doxorubicin, vinblastin and methotrexate-based free, adjuvant external beam radiation was planned.
chemotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (imatinib, Radiation by conventional techniques leads to
sorafinib) have also been used in recurrent progressive increased doses to adjacent normal structures (lungs
tumors after surgery. and breast in this case), which may lead to late
complications in the form of fibrosis or secondary
The overall rate of recurrence ranges between malignancies. However, with the use of newer
25% and 75%. There is a huge variation in rate in
the literature. [9,13] Although survival at 5 years is techniques, it is possible to give homogenous dose
distribution to the target volume, while keeping
nearly 93%, the probability of recurrence is an
estimated 29%. [14] Even though these tumors do not the dose to critical and normal structures within
metastasize, they can result in significant morbidity normal range. In our case, we chose image-guided
and death from locoregional invasion. [15] The role intensity modulated radiotherapy technique to spare
of adjuvant radiotherapy after surgical resection maximum normal tissues (adjacent breast and lung
of primary disease is controversial and should parenchyma). Tolerance of lungs and heart was
be based on a balanced discussion of potential well respected. This case provides valuable insights
morbidity from radiotherapy and recurrence. The into potential treatment approaches in such a rare
local control of desmoid tumor in the adjuvant setting presentation.
is excellent, with total doses ranging from 50-60 Gy,
with acceptable morbidity. Margin status is one of the Authors’ contributions
most important predictor of recurrence after surgery Writing and conceptualization of this work: R. Agrawal,
in desmoid tumors. If a future local recurrence would P. Choudhary
incur even greater morbidity or would be potentially Supervising the work: V. Zamre, A.K. Goel, S. Agarwal,
unresectable, then adding adjuvant radiotherapy D. Singh
would be reasonable. The benefit of radiotherapy
has been claimed in several reports. In particular, Financial support and sponsorship
a review by Nuyttens et al. [16] including more than None.
20 retrospective studies focusing on the role of the
combination (surgery and radiotherapy), showed Conflicts of interest
that surgery plus radiotherapy or radiotherapy alone There are no conflicts of interest.
could obtain a better local control rate (75% and
78%, respectively) compared with surgery alone Patient consent
(61%). However, this is an extremely debated topic. Patient’s consent was obtained as per institutional
According to Gronchi et al., [17] these tumors represent policy.
a relatively benign condition and most of the patients
are young; hence the authors suggest radiotherapy Ethics approval
only for documented progressive disease and in The ethics approval was obtained from the institutional
absence of other alternatives. Table 1 shows some ethical committee for preparation and publication of
literature on chest wall fibromatoses with their this paper.
142 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ July 21, 2017