Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
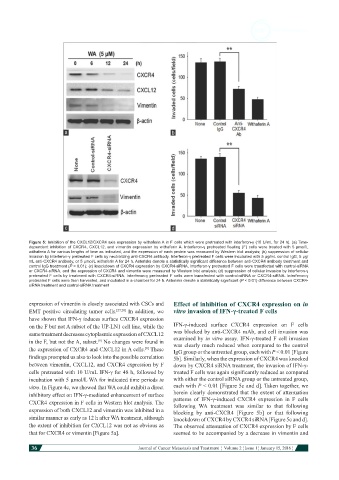
Figure 5: Inhibition of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis expression by withaferin A in F cells which were pretreated with interferon-γ (10 U/mL for 24 h). (a) Time-
dependent inhibition of CXCR4, CXCL12, and vimentin expression by withaferin A. Interferon-γ pretreated floating (F) cells were treated with 5 μmol/L
withaferin A for various lengths of time as indicated, and the expression of each protein was measured by Western blot analysis; (b) suppression of cellular
invasion by interferon-γ pretreated F cells by neutralizing anti-CXCR4 antibody. Interferon-γ pretreated F cells were incubated with 5 μg/mL control IgG, 5 μg/
mL anti-CXCR4 antibody, or 5 μmol/L withaferin A for 24 h. Asterisks denote a statistically significant difference between anti-CXCR4 antibody treatment and
control IgG treatment (P < 0.01); (c) knockdown of CXCR4 expression by CXCR4-siRNA. Interferon-γ pretreated F cells were transfected with control-siRNA
or CXCR4-siRNA, and the expression of CXCR4 and vimentin were measured by Western blot analysis; (d) suppression of cellular invasion by interferon-γ
pretreated F cells by treatment with CXCR4-siRNA. Interferon-γ pretreated F cells were transfected with control-siRNA or CXCR4-siRNA. Interferon-γ
pretreated F cells were then harvested, and incubated in a chamber for 24 h. Asterisks denote a statistically significant (P < 0.01) difference between CXCR4-
siRNA treatment and control-siRNA treatment
expression of vimentin is closely associated with CSCs and Effect of inhibition of CXCR4 expression on in
EMT positive circulating tumor cells. [27,28] In addition, we vitro invasion of IFN-γ-treated F cells
have shown that IFN-γ induces surface CXCR4 expression
on the F but not A subset of the UP-LN1 cell line, while the IFN-γ-induced surface CXCR4 expression on F cells
same treatment decreases cytoplasmic expression of CXCL12 was blocked by anti-CXCR4 mAb, and cell invasion was
in the F, but not the A, subset. No changes were found in examined by in vitro assay. IFN-γ-treated F cell invasion
[9]
was clearly much reduced when compared to the control
the expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in A cells. These IgG group or the untreated group, each with P < 0.01 [Figure
[9]
findings prompted us also to look into the possible correlation 5b]. Similarly, when the expression of CXCR4 was knocked
between vimentin, CXCL12, and CXCR4 expression by F down by CXCR4 siRNA treatment, the invasion of IFN-γ-
cells pretreated with 10 U/mL IFN-γ for 48 h, followed by treated F cells was again significantly reduced as compared
incubation with 5 µmol/L WA for indicated time periods in with either the control siRNA group or the untreated group,
vitro. In Figure 4c, we showed that WA could exhibit a direct each with P < 0.01 [Figure 5c and d]. Taken together, we
inhibitory effect on IFN-γ-mediated enhancement of surface herein clearly demonstrated that the extent of attenuation
CXCR4 expression in F cells in Western blot analysis. The patterns of IFN-γ-induced CXCR4 expression in F cells
following WA treatment was similar to that following
expression of both CXCL12 and vimentin was inhibited in a blocking by anti-CXCR4 [Figure 5b] or that following
similar manner as early as 12 h after WA treatment, although knockdown of CXCR4 by CXCR4 siRNA [Figure 5c and d].
the extent of inhibition for CXCL12 was not as obvious as The observed attenuation of CXCR4 expression by F cells
that for CXCR4 or vimentin [Figure 5a]. seemed to be accompanied by a decrease in vimentin and
36
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ Issue 1 ¦ January 15, 2016 ¦