Page 45 - Read Online
P. 45
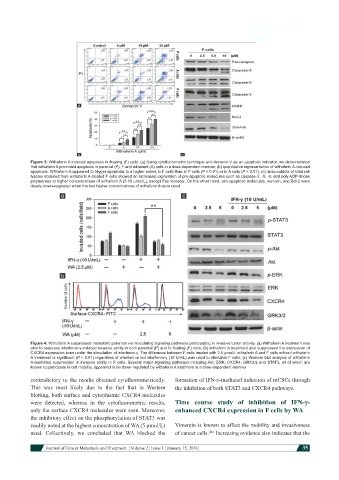
Figure 3: Withaferin A induced apoptosis in floating (F) cells. (a) Using cytofluorometric technique and Annexin V as an apoptotic indicator, we demonstrated
that withaferin A promoted apoptosis in parental (P), F and adherent (A) cells in a dose-dependent manner; (b) quantitative representation of withaferin A-induced
apoptosis. Withaferin A appeared to trigger apoptosis to a higher extent in F cells than in P cells (P < 0.01) or in A cells (P < 0.01); (c) immunoblots of total cell
lysates obtained from withaferin A-treated F cells showed an increased expression of pro-apoptotic molecules such as caspase-3, -8, -9, and poly ADP-ribose
polymerase at higher concentrations of withaferin A (5-10 μmol/L), except Fas receptor. On the other hand, anti-apoptotic molecules, survivin, and Bcl-2 were
clearly down-regulated when the two higher concentrations of withaferin A were used
Figure 4: Withaferin A suppressed metastatic potential via modulating signaling pathways participating in invasive tumor activity. (a) Withaferin A treatment was
able to suppress interferon-γ-induced invasive ability in both parental (P) and to floating (F) cells; (b) withaferin A treatment also suppressed the expression of
CXCR4 expression even under the stimulation of interferon-γ. The difference between F cells treated with 2.5 μmol/L withaferin A and F cells without withaferin
A treatment is significant (P < 0.01) regardless of whether or not interferon-γ (10 U/mL) was used to stimulate F cells; (c) Western blot analysis of withaferin
A-mediated suppression in invasive ability in F cells. Several major signaling pathways including Akt, ERK, CXCR4, GRK3/2 and STAT3, all of which are
known to participate in cell mobility, appeared to be down-regulated by withaferin A treatment in a dose-dependent manner
contradictory to the results obtained cytofluorometrically. formation of IFN-γ-mediated induction of mCSCs through
This was most likely due to the fact that in Western the inhibition of both STAT3 and CXCR4 pathways.
blotting, both surface and cytoplasmic CXCR4 molecules
were detected, whereas in the cytofluorometric results, Time course study of inhibition of IFN-γ-
only the surface CXCR4 molecules were seen. Moreover, enhanced CXCR4 expression in F cells by WA
the inhibitory effect on the phosphorylation of STAT3 was
readily noted at the highest concentration of WA (5 μmol/L) Vimentin is known to affect the mobility and invasiveness
used. Collectively, we concluded that WA blocked the of cancer cells. Increasing evidence also indicates that the
[26]
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ Issue 1 ¦ January 15, 2016 ¦ 35