Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
Page 271 Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):256-75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.17
Table 4. Accuracy comparison of bundle adjustment
Parallel algorithm error (pixel) Serial algorithm error(pixel)
Data id Number of edges Original error
1 iteration 10 iterations 1 iteration 10 iterations
0 64,201 0.588 0.549 0.500 0.549 0.500
1 135,702 0.579 0.549 0.502 0.549 0.502
2 185,364 0.562 0.538 0.500 0.538 0.500
3 239,182 0.563 0.542 0.511 0.542 0.511
4 289,890 0.547 0.530 0.503 0.530 0.503
5 348,542 0.555 0.530 0.503 0.530 0.503
6 402,374 0.544 0.523 0.500 0.523 0.500
7 458,623 0.569 0.543 0.522 0.543 0.522
8 511,519 0.575 0.551 0.523 0.551 0.523
9 561,116 0.629 0.600 0.570 0.600 0.570
Table 5. Thread parameters for different tasks
Section BlockDim.x BlockDim.y GridDim.x GridDim.y
Image pyramid min(64, +32−1 × 32) 2 + . −1 + . −1
32 . .
Fast corner + . −1 + . −1
detection 32 4 . .
Non-maximal
max(1, min[ 128 , ])
suppression
Direction
calculation 32 8 1 .
Descriptor
calculation 32 8 1 .
Creating linear
structures 32 32 32∗32 1
Error
calculations 32 16 32 1
Building linear
systems 512 1 512 1
Solving linear
systems 512 1 . 1
(1) BlockDim and GridDim is the size of the thread block and thread grid
(2) and is the size of the image, where represents the level of the current image pyramid
Note (3) and is the size of the grid used in non-maximal suppression
(4) is the number of the edges in BA
(5) is the number of the calculation to the or
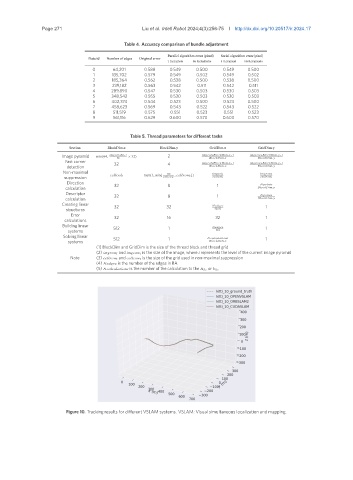
Figure 10. Tracking results for different VSLAM systems. VSLAM: Visual simultaneous localization and mapping.