Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):256-75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.17 Page 272
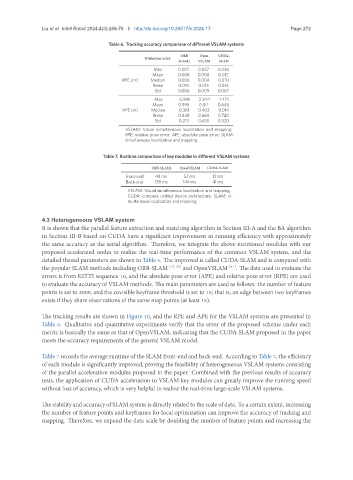
Table 6. Tracking accuracy comparison of different VSLAM systems
ORB Open CUDA-
Evaluation index
SLAM2 VSLAM SLAM
Max 0.027 0.057 0.036
Mean 0.008 0.008 0.012
RPE (m) Median 0.006 0.004 0.010
Rmse 0.010 0.013 0.014
Std 0.006 0.009 0.007
Max 0.991 2.344 1.474
Mean 0.395 0.511 0.645
APE (m) Median 0.361 0.402 0.014
Rmse 0.448 0.684 0.720
Std 0.213 0.455 0.320
VSLAM: Visual simultaneous localization and mapping;
RPE: relative pose error; APE: absolute pose error; SLAM:
simultaneous localization and mapping.
Table 7. Runtime comparison of key modules in different VSLAM systems
ORB-SLAM2 OpenVSLAM CUDA-SLAM
Front-end 48 ms 52 ms 12 ms
Back-end 138 ms 144 ms 41 ms
VSLAM: Visual simultaneous localization and mapping;
CUDA: compute unified device architecture; SLAM: si-
multaneous localization and mapping.
4.3 Heterogeneous VSLAM system
It is shown that the parallel feature extraction and matching algorithm in Section III-A and the BA algorithm
in Section III-B based on CUDA have a significant improvement in running efficiency with approximately
the same accuracy as the serial algorithm. Therefore, we integrate the above-mentioned modules with our
proposed accelerated nodes to realize the real-time performance of the common VSLAM system, and the
detailed thread parameters are shown in Table 5. The improved is called CUDA-SLAM and is compared with
the popular SLAM methods including ORB-SLAM [17,18] and OpenVSLAM [31] . The data used to evaluate the
errors is from KITTI sequence 10, and the absolute pose error (APE) and relative pose error (RPE) are used
to evaluate the accuracy of VSLAM methods. The main parameters are used as follows: the number of feature
points is set to 2000, and the covisible keyframe threshold is set to 15; that is, an edge between two keyframes
exists if they share observations of the same map points (at least 15).
The tracking results are shown in Figure 10, and the RPE and APE for the VSLAM systems are presented in
Table 6. Qualitative and quantitative experiments verify that the error of the proposed scheme under each
metric is basically the same as that of OpenVSLAM, indicating that the CUDA-SLAM proposed in the paper
meets the accuracy requirements of the general VSLAM model.
Table 7 records the average runtime of the SLAM front-end and back-end. According to Table 7, the efficiency
of each module is significantly improved, proving the feasibility of heterogeneous VSLAM systems consisting
of the parallel acceleration modules proposed in the paper. Combined with the previous results of accuracy
tests, the application of CUDA acceleration to VSLAM key modules can greatly improve the running speed
without loss of accuracy, which is very helpful to realize the real-time large-scale VSLAM systems.
ThestabilityandaccuracyofSLAMsystemis directlyrelated tothescale ofdata. Toacertain extent, increasing
the number of feature points and keyframes for local optimization can improve the accuracy of tracking and
mapping. Therefore, we expand the data scale by doubling the number of feature points and increasing the