Page 89 - Read Online
P. 89
Page 273 Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):256-75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.17
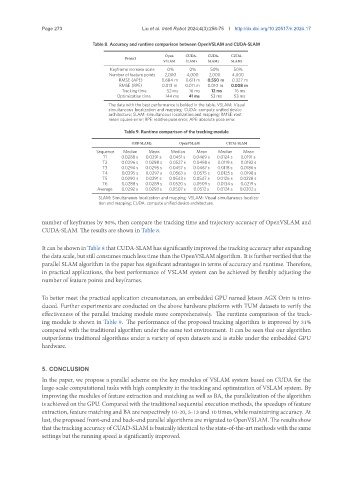
Table 8. Accuracy and runtime comparison between OpenVSLAM and CUDA-SLAM
Open CUDA- CUDA- CUDA-
Project
VSLAM SLAM1 SLAM2 SLAM3
Keyframe increase scale 0% 0% 50% 50%
Number of feature points 2,000 4,000 2,000 4,000
RMSE (APE) 0.684 m 0.611 m 0.550 m 0.327 m
RMSE (RPE) 0.013 m 0.011 m 0.010 m 0.008 m
Tracking time 52 ms 16 ms 12 ms 16 ms
Optimization time 144 ms 41 ms 53 ms 53 ms
The data with the best performance is bolded in the table. VSLAM: Visual
simultaneous localization and mapping; CUDA: compute unified device
architecture; SLAM: simultaneous localization and mapping; RMSE: root
mean square error; RPE: relative pose error; APE: absolute pose error.
Table 9. Runtime comparison of the tracking module
ORB-SLAM2 OpenVSLAM CUDA-SLAM
Sequence Median Mean Median Mean Median Mean
T1 0.0288 s 0.0291 s 0.0451 s 0.0469 s 0.0124 s 0.0191 s
T2 0.0296 s 0.0298 s 0.0527 s 0.0498 s 0.0119 s 0.0192 s
T3 0.0294 s 0.0295 s 0.0457 s 0.0467 s 0.0118 s 0.0186 s
T4 0.0295 s 0.0297 s 0.0563 s 0.0575 s 0.0125 s 0.0198 s
T5 0.0290 s 0.0291 s 0.0543 s 0.0547 s 0.0126 s 0.0228 s
T6 0.0288 s 0.0289 s 0.0520 s 0.0509 s 0.0134 s 0.0219 s
Average 0.0292 s 0.0293 s 0.0507 s 0.0512 s 0.0124 s 0.0202 s
SLAM: Simultaneous localization and mapping; VSLAM: Visual simultaneous localiza-
tion and mapping; CUDA: compute unified device architecture.
number of keyframes by 50%, then compare the tracking time and trajectory accuracy of OpenVSLAM and
CUDA-SLAM. The results are shown in Table 8.
It can be shown in Table 8 that CUDA-SLAM has significantly improved the tracking accuracy after expanding
the data scale, but still consumes much less time than the OpenVSLAM algorithm. It is further verified that the
parallel SLAM algorithm in the paper has significant advantages in terms of accuracy and runtime. Therefore,
in practical applications, the best performance of VSLAM system can be achieved by flexibly adjusting the
number of feature points and keyframes.
To better meet the practical application circumstances, an embedded GPU named Jetson AGX Orin is intro-
duced. Further experiments are conducted on the above hardware platform with TUM datasets to verify the
effectiveness of the parallel tracking module more comprehensively. The runtime comparison of the track-
ing module is shown in Table 9. The performance of the proposed tracking algorithm is improved by 31%
compared with the traditional algorithm under the same test environment. It can be seen that our algorithm
outperforms traditional algorithms under a variety of open datasets and is stable under the embedded GPU
hardware.
5. CONCLUSION
In the paper, we propose a parallel scheme on the key modules of VSLAM system based on CUDA for the
large-scale computational tasks with high complexity in the tracking and optimization of VSLAM system. By
improving the modules of feature extraction and matching as well as BA, the parallelization of the algorithm
is achieved on the GPU. Compared with the traditional sequential execution methods, the speedups of feature
extraction, feature matching and BA are respectively 10-20, 5-13 and 10 times, while maintaining accuracy. At
last, the proposed front-end and back-end parallel algorithms are migrated to OpenVSLAM. The results show
that the tracking accuracy of CUAD-SLAM is basically identical to the state-of-the-art methods with the same
settings but the running speed is significantly improved.