Page 82 - Read Online
P. 82
Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):256-75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.17 Page 266
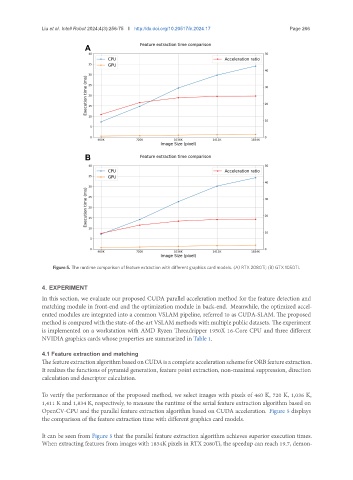
Figure 5. The runtime comparison of feature extraction with different graphics card models. (A) RTX 2080Ti; (B) GTX 1050Ti.
4. EXPERIMENT
In this section, we evaluate our proposed CUDA parallel acceleration method for the feature detection and
matching module in front-end and the optimization module in back-end. Meanwhile, the optimized accel-
erated modules are integrated into a common VSLAM pipeline, referred to as CUDA-SLAM. The proposed
method is compared with the state-of-the-art VSLAM methods with multiple public datasets. The experiment
is implemented on a workstation with AMD Ryzen Threadripper 1950X 16-Core CPU and three different
NVIDIA graphics cards whose properties are summarized in Table 1.
4.1 Feature extraction and matching
ThefeatureextractionalgorithmbasedonCUDAisacompleteaccelerationschemeforORBfeatureextraction.
It realizes the functions of pyramid generation, feature point extraction, non-maximal suppression, direction
calculation and descriptor calculation.
To verify the performance of the proposed method, we select images with pixels of 460 K, 720 K, 1,036 K,
1,411 K and 1,834 K, respectively, to measure the runtime of the serial feature extraction algorithm based on
OpenCV-CPU and the parallel feature extraction algorithm based on CUDA acceleration. Figure 5 displays
the comparison of the feature extraction time with different graphics card models.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the parallel feature extraction algorithm achieves superior execution times.
When extracting features from images with 1834K pixels in RTX 2080Ti, the speedup can reach 19.7, demon-