Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Castán et al. Radiology of hepatocarcinoma in non-cirrhotic patients
A B C
Figure 13: Computed tomography of axial planes obtained in empty (A), arterial phase (B), and portal phase (C). It shows healthy liver with
hypodense mass in empty (A) with intense enhancement in the arterial phase (B), and washed-out in portal phase (C). The first radiological
and pathological diagnosis was hepatic adenoma. A second biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
(5-10%). It is more common in men with deposition late phase, due to the slowness of washing related to
diseases or who consume anabolic steroids. the fibrous tissue in the tumor [Figure 14]. The pattern
of progressive or stable enhancement in portal and
HCC should be distinguished from ICC with mass late phases can also sometimes be observed in HCC.
growth pattern. Although they are malignant tumors, Therefore, with this type of pattern we always perform
prognosis and treatment are very different in both a biopsy for histological diagnosis.
entities. The typical enhancement pattern of ICC is
a gradual contrast uptake without washing (80% of Liver can also be a frequent site of metastatic
ICC) or stable contrast uptake without washing (20% neuroendocrine tumors from another location [Figure 15]; it
of ICC). In arterial phase, it appears as a hypodense is unlikely to be of primary liver origin. The primary
mass with incomplete peripheral enhancement. The hepatic carcinoid tumor appears as a liver mass,
central part shows a prolonged enhancement in the usually solid (60%), partially solid with cystic areas
A B
C D
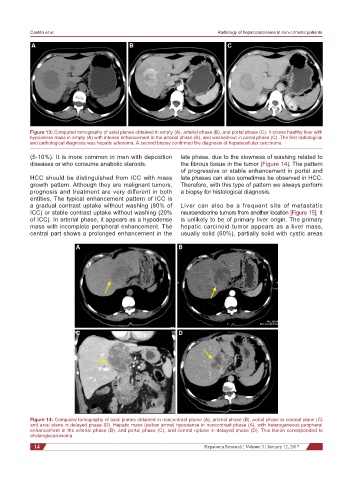
Figure 14: Computed tomography of axial planes obtained in noncontrast phase (A), arterial phase (B), portal phase in coronal plane (C)
and axial plane in delayed phase (D). Hepatic mass (yellow arrow) hypodense in noncontrast phase (A), with heterogeneous peripheral
enhancement in the arterial phase (B), and portal phase (C), and central uptake in delayed phase (D). This lesion corresponded to
cholangiocarcinoma
14 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ January 12, 2017