Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
showed that there was no cytotoxicity at < 10 μmol/L of used as a target of the JNK pathway. Inversely, HBx protein
sorafenib [Figure 1e]. In addition, mRNA and protein levels of levels were increased by JNK overexpression [Figure 2d] and
HBx or core, HBV gene products, were decreased by sorafenib HBV promoter activity and HBx expression induced by JNK1
in a dose-dependent manner [Figure 1f and g]. These results were attenuated by sorafenib [Figure 2e and f]. These results
suggest that sorafenib may suppress HBV gene expression suggest that sorafenib may suppress HBV gene expression
regardless of cell death. through JNK pathway inhibition.
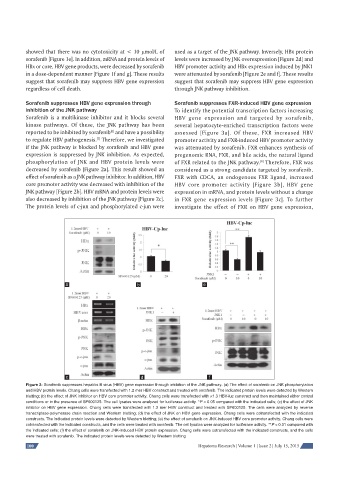
Sorafenib suppresses HBV gene expression through Sorafenib suppresses FXR-induced HBV gene expression
inhibition of the JNK pathway To identify the potential transcription factors increasing
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor and it blocks several HBV gene expression and targeted by sorafenib,
kinase pathways. Of these, the JNK pathway has been several hepatocyte-enriched transcription factors were
[6]
reported to be inhibited by sorafenib and have a possibility assessed [Figure 3a]. Of these, FXR increased HBV
[7]
to regulate HBV pathogenesis. Therefore, we investigated promoter activity and FXR-induced HBV promoter activity
if the JNK pathway is blocked by sorafenib and HBV gene was attenuated by sorafenib. FXR enhances synthesis of
expression is suppressed by JNK inhibition. As expected, pregenomic RNA, FXR, and bile acids, the natural ligand
phosphorylation of JNK and HBV protein levels were of FXR related to the JNK pathway. Therefore, FXR was
[8]
decreased by sorafenib [Figure 2a]. This result showed an considered as a strong candidate targeted by sorafenib.
effect of sorafenib as a JNK pathway inhibitor. In addition, HBV FXR with CDCA, an endogenous FXR ligand, increased
core promoter activity was decreased with inhibition of the HBV core promoter activity [Figure 3b], HBV gene
JNK pathway [Figure 2b]. HBV mRNA and protein levels were expression in mRNA, and protein levels without a change
also decreased by inhibition of the JNK pathway [Figure 2c]. in FXR gene expression levels [Figure 3c]. To further
The protein levels of c-jun and phosphorylated c-jun were investigate the effect of FXR on HBV gene expression,
a b e
c d f
Figure 2: Sorafenib suppresses hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression through inhibition of the JNK pathway. (a) The effect of sorafenib on JNK phosphorylation
and HBV protein levels. Chang cells were transfected with 1.2 mer HBV construct and treated with sorafenib. The indicated protein levels were detected by Western
blotting; (b) the effect of JNK inhibitor on HBV core promoter activity. Chang cells were transfected with ×1.3 HBV-luc construct and then maintained either control
conditions or in the presence of SP600125. The cell lysates were analyzed for luciferase activity. *P < 0.05 compared with the indicated cells; (c) the effect of JNK
inhibitor on HBV gene expression. Chang cells were transfected with 1.2 mer HBV construct and treated with SP600125. The cells were analyzed by reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting; (d) the effect of JNK on HBV gene expression. Chang cells were cotransfected with the indicated
constructs. The indicated protein levels were detected by Western blotting; (e) the effect of sorafenib on JNK-induced HBV core promoter activity. Chang cells were
cotransfected with the indicated constructs, and the cells were treated with sorafenib. The cell lysates were analyzed for luciferase activity. **P < 0.01 compared with
the indicated cells; (f) the effect of sorafenib on JNK-induced HBV protein expression. Chang cells were cotransfected with the indicated constructs, and the cells
were treated with sorafenib. The indicated protein levels were detected by Western blotting
100 Hepatoma Research | Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July 15, 2015