Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Page 8 of 12 Zhang et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400043 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2023.102
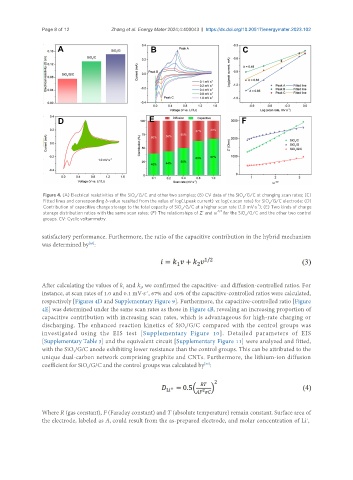
Figure 4. (A) Electrical resistivities of the SiO /G/C and other two samples; (B) CV data of the SiO /G/C at changing scan rates; (C)
x
x
Fitted lines and corresponding b-value resulted from the value of log(i, peak current) vs. log(v, scan rate) for SiO /G/C electrode; (D)
x
-1
Contribution of capacitive charge storage to the total capacity of SiO /G/C at a higher scan rate (1.0 mV·s ); (E) Two kinds of charge
x
storage distribution ratios with the same scan rates; (F) The relationships of Z’ and ω -1/2 for the SiO /G/C and the other two control
x
groups. CV: Cyclic voltammetry.
satisfactory performance. Furthermore, the ratio of the capacitive contribution in the hybrid mechanism
was determined by :
[45]
After calculating the values of k and k , we confirmed the capacitive- and diffusion-controlled ratios. For
2
1
instance, at scan rates of 1.0 and 0.1 mV·s , 67% and 40% of the capacitive-controlled ratios were calculated,
-1
respectively [Figures 4D and Supplementary Figure 9]. Furthermore, the capacitive-controlled ratio [Figure
4E] was determined under the same scan rates as those in Figure 4B, revealing an increasing proportion of
capacitive contribution with increasing scan rates, which is advantageous for high-rate charging or
discharging. The enhanced reaction kinetics of SiO /G/C compared with the control groups was
x
investigated using the EIS test [Supplementary Figure 10]. Detailed parameters of EIS
[Supplementary Table 3] and the equivalent circuit [Supplementary Figure 11] were analyzed and fitted,
with the SiO /G/C anode exhibiting lower resistance than the control groups. This can be attributed to the
x
unique dual-carbon network comprising graphite and CNTs. Furthermore, the lithium-ion diffusion
[33]
coefficient for SiO /G/C and the control groups was calculated by :
x
Where R (gas constant), F (Faraday constant) and T (absolute temperature) remain constant. Surface area of
the electrode, labeled as A, could result from the as-prepared electrode, and molar concentration of Li ,
+