Page 34 - Read Online
P. 34
Zhang et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400043 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2023.102 Page 7 of 12
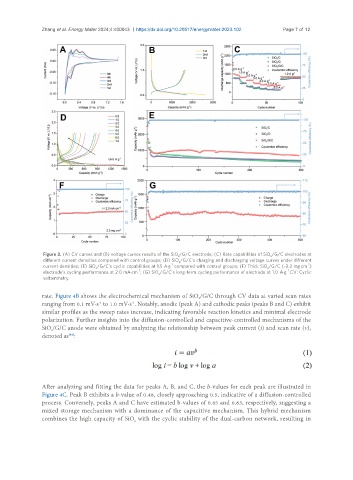
Figure 3. (A) CV curves and (B) voltage curves results of the SiO /G/C electrode; (C) Rate capabilities of SiO /G/C electrodes at
x
x
different current densities compared with control groups; (D) SiO /G/C’s charging and discharging voltage curves under different
x
-1
-2
current densities; (E) SiO /G/C’s cyclic capabilities at 1.5 A·g compared with control groups; (F) Thick SiO /G/C (~2.2 mg·cm )
x
x
-1
-2
electrode’s cycling performance at 2.0 mA·cm ; (G) SiO /G/C’s long-term cycling performance of electrode at 1.0 A·g . CV: Cyclic
x
voltammetry.
rate. Figure 4B shows the electrochemical mechanism of SiO /G/C through CV data at varied scan rates
x
-1
-1
ranging from 0.1 mV·s to 1.0 mV·s . Notably, anodic (peak A) and cathodic peaks (peaks B and C) exhibit
similar profiles as the sweep rates increase, indicating favorable reaction kinetics and minimal electrode
polarization. Further insights into the diffusion-controlled and capacitive-controlled mechanisms of the
SiO /G/C anode were obtained by analyzing the relationship between peak current (i) and scan rate (v),
x
denoted as :
[44]
After analyzing and fitting the data for peaks A, B, and C, the b-values for each peak are illustrated in
Figure 4C. Peak B exhibits a b-value of 0.48, closely approaching 0.5, indicative of a diffusion-controlled
process. Conversely, peaks A and C have estimated b-values of 0.85 and 0.63, respectively, suggesting a
mixed storage mechanism with a dominance of the capacitive mechanism. This hybrid mechanism
combines the high capacity of SiO with the cyclic stability of the dual-carbon network, resulting in
x