Page 96 - Read Online
P. 96
Mao et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:26 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.41 Page 23 of 33
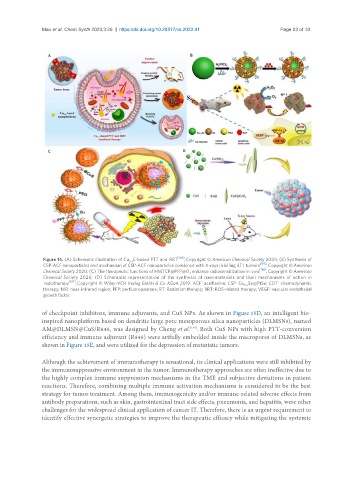
Figure 14. (A) Schematic illustration of Cu E-based PTT and RRT [184] , Copyright © American Chemical Society 2020; (B) Synthesis of
2-x
CSP-ACF nanoparticles and mechanism of CSP-ACF nanoparticles combined with X-rays in killing 4T1 tumors [185] , Copyright © American
Chemical Society 2020; (C) The therapeutic functions of HMTCP@PFP@O enhance radiosensitization in vivo [186] , Copyright © American
2
Chemical Society 2020; (D) Schematic representation of the synthesis of nanomaterials and their mechanisms of action in
radiotherapy [187] , Copyright © Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA 2019. ACF: acriflavine; CSP: Cu Se@PtSe; CDT: chemodynamic
2-x
therapy; NIR: near-infrared region; PFP: perfluoropentane; RT: Radiation therapy; RRT: ROS-related therapy; VEGF: vascular endothelial
growth factor.
of checkpoint inhibitors, immune adjuvants, and CuS NPs. As shown in Figure 15D, an intelligent bio-
inspired nanoplatform based on dendritic large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles (DLMSNs), named
AM@DLMSN@CuS/R848, was designed by Cheng et al. . Both CuS NPs with high PTT-conversion
[149]
efficiency and immune adjuvant (R848) were artfully embedded inside the macropores of DLMSNs, as
shown in Figure 15E, and were utilized for the depression of metastatic tumors.
Although the achievement of immunotherapy is sensational, its clinical applications were still inhibited by
the immunosuppressive environment in the tumor. Immunotherapy approaches are often ineffective due to
the highly complex immune suppression mechanisms in the TME and subjective deviations in patient
reactions. Therefore, combining multiple immune activation mechanisms is considered to be the best
strategy for tumor treatment. Among them, immunogenicity and/or immune-related adverse effects from
antibody preparations, such as skin, gastrointestinal tract side effects, pneumonia, and hepatitis, were other
challenges for the widespread clinical application of cancer IT. Therefore, there is an urgent requirement to
identify effective synergetic strategies to improve the therapeutic efficacy while mitigating the systemic