Page 178 - Read Online
P. 178
Harangi et al. HDL structure and function in dyslipidemia
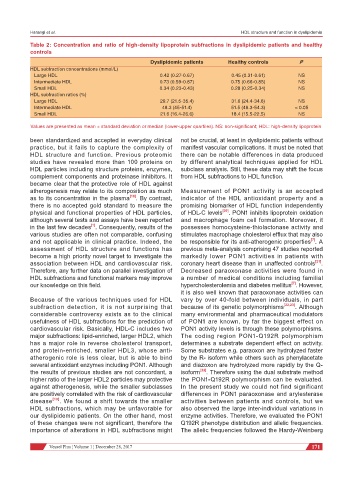
Table 2: Concentration and ratio of high-density lipoprotein subfractions in dyslipidemic patients and healthy
controls
Dyslipidemic patients Healthy controls P
HDL subfraction concentrations (mmol/L)
Large HDL 0.42 (0.27-0.67) 0.45 (0.31-0.61) NS
Intermediate HDL 0.73 (0.59-0.87) 0.75 (0.66-0.85) NS
Small HDL 0.34 (0.23-0.43) 0.28 (0.25-0.34) NS
HDL subfraction ratios (%)
Large HDL 29.7 (21.5-35.4) 31.6 (24.4-34.6) NS
Intermediate HDL 48.3 (45-51.4) 51.5 (48.3-54.3) < 0.05
Small HDL 21.6 (16.4-26.6) 18.4 (15.5-22.5) NS
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation or median (lower-upper quartiles). NS: non-significant; HDL: high-density lipoprotein
been standardized and accepted in everyday clinical not be crucial, at least in dyslipidemic patients without
practice, but it fails to capture the complexity of manifest vascular complications. It must be noted that
HDL structure and function. Previous proteomic there can be notable differences in data produced
studies have revealed more than 100 proteins on by different analytical techniques applied for HDL
HDL particles including structure proteins, enzymes, subclass analysis. Still, these data may shift the focus
complement components and proteinase inhibitors. It from HDL subfractions to HDL function.
became clear that the protective role of HDL against
atherogenesis may relate to its composition as much Measurement of PON1 activity is an accepted
as to its concentration in the plasma [18] . By contrast, indicator of the HDL antioxidant property and a
there is no accepted gold standard to measure the promising biomarker of HDL function independently
physical and functional properties of HDL particles, of HDL-C levels [20] . PON1 inhibits lipoprotein oxidation
although several tests and assays have been reported and macrophage foam cell formation. Moreover, it
[1]
in the last few decades . Consequently, results of the possesses homocysteine-thiolactonase activity and
various studies are often not comparable, confusing stimulates macrophage cholesterol efflux that may also
[7]
and not applicable in clinical practice. Indeed, the be responsible for its anti-atherogenic properties . A
assessment of HDL structure and functions has previous meta-analysis comprising 47 studies reported
become a high priority novel target to investigate the markedly lower PON1 activities in patients with
association between HDL and cardiovascular risk. coronary heart disease than in unaffected controls [21] .
Therefore, any further data on parallel investigation of Decreased paraoxonase activities were found in
HDL subfractions and functional markers may improve a number of medical conditions including familial
[7]
our knowledge on this field. hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus . However,
it is also well known that paraoxonase activities can
Because of the various techniques used for HDL vary by over 40-fold between individuals, in part
subfraction detection, it is not surprising that because of its genetic polymorphisms [22,23] . Although
considerable controversy exists as to the clinical many environmental and pharmaceutical modulators
usefulness of HDL subfractions for the prediction of of PON1 are known, by far the biggest effect on
cardiovascular risk. Basically, HDL-C includes two PON1 activity levels is through these polymorphisms.
major subfractions: lipid-enriched, larger HDL2, which The coding region PON1-Q192R polymorphism
has a major role in reverse cholesterol transport, determines a substrate dependent effect on activity.
and protein-enriched, smaller HDL3, whose anti- Some substrates e.g. paraoxon are hydrolyzed faster
atherogenic role is less clear, but is able to bind by the R- isoform while others such as phenylacetate
several antioxidant enzymes including PON1. Although and diazoxon are hydrolyzed more rapidly by the Q-
the results of previous studies are not concordant, a isoform [22] . Therefore using the dual substrate method
higher ratio of the larger HDL2 particles may protective the PON1-Q192R polymorphism can be evaluated.
against atherogenesis, while the smaller subclasses In the present study we could not find significant
are positively correlated with the risk of cardiovascular differences in PON1 paraoxonase and arylesterase
disease [19] . We found a shift towards the smaller activities between patients and controls, but we
HDL subfractions, which may be unfavorable for also observed the large inter-individual variations in
our dyslipidemic patients. On the other hand, most enzyme activities. Therefore, we evaluated the PON1
of these changes were not significant, therefore the Q192R phenotype distribution and allelic frequencies.
importance of alterations in HDL subfractions might The allelic frequencies followed the Hardy-Weinberg
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 171