Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Dong et al. UPI peptide as cancer therapeutic
A CTR UPI C
TC
LLC CTR RBC
CD31 CD31
U87 RBC RBC
CD31 CD31 UPI
TC
B
D CTR UPI
CTR VEGFR2
CD31 FITC Merge LLC
Tubulin
VEGFR2
UPI U87
Tubulin
CD31 FITC Merge
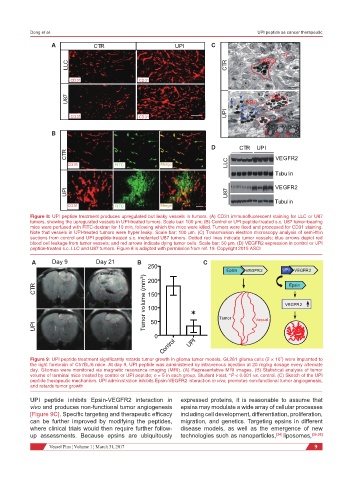
Figure 8: UPI peptide treatment produces upregulated but leaky vessels in tumors. (A) CD31 immunofluorescent staining for LLC or U87
tumors, showing the upregulated vessels in UPI-treated tumors. Scale bar: 100 µm; (B) Control or UPI peptide-treated s.c. U87 tumor-bearing
mice were perfused with FITC-dextran for 10 min, following which the mice were killed. Tumors were fixed and processed for CD31 staining.
Note that vessels in UPI-treated tumors were hyper leaky. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of semi-thin
sections from control and UPI peptide-treated s.c. implanted U87 tumors. Dotted red lines indicate tumor vessels; blue arrows depict red
blood cell leakage from tumor vessels; and red arrows indicate dying tumor cells. Scale bar: 50 µm. (D) VEGFR2 expression in control or UPI
peptide-treated s.c. LLC and U87 tumors. Figure 8 is adapted with permission from ref. 19. Copyright 2015 ASCI
A Day 9 Day 21 B C
250
Epsin VEGFR2 UPI VEGFR2
Tumor volume (mm 3 ) 100 * VEGFR2
CTR 200 Epsin
150
UPI 50 Tumor Vessel
0
4
Figure 9: UPI peptide treatment significantly retards tumor growth in glioma tumor models. GL261 glioma cells (2 × 10 ) were implanted to
the right forebrain of C57BL/6 mice. At day 9, UPI peptide was administered by intravenous injection at 20 mg/kg dosage every alternate
day. Gliomas were monitored via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (A) Representative MRI images. (B) Statistical analysis of tumor
volume of terminal mice treated by control or UPI peptide; n = 5 in each group, Student t-test, *P < 0.001 vs. control. (C) Sketch of the UPI
peptide therapeutic mechanism. UPI administration inhibits Epsin-VEGFR2 interaction in vivo, promotes non-functional tumor angiogenesis,
and retards tumor growth
UPI peptide inhibits Epsin-VEGFR2 interaction in expressed proteins, it is reasonable to assume that
vivo and produces non-functional tumor angiogenesis epsins may modulate a wide array of cellular processes
[Figure 9C]. Specific targeting and therapeutic efficacy including cell development, differentiation, proliferation,
can be further improved by modifying the peptides, migration, and genetics. Targeting epsins in different
where clinical trials would then require further follow- disease models, as well as the emergence of new
up assessments. Because epsins are ubiquitously technologies such as nanoparticles, [34] liposomes, [35,36]
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017 9