Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Dong et al. UPI peptide as cancer therapeutic
A B vivo. In cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells
(HUVECs), the UPI peptide treatment had no effect on
other angiogenic growth factor signaling such as epidermal
growth factor receptor (EGFR), platelet-derived growth
factor receptor (PDGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptor
(FGFR), and transforming growth factor beta (TGFb)
pathways. We previously obtained similar results in
[19]
C D UPI-treated mouse tumors. This targeting specificity
[19]
may be interpreted from the length of the UIM. It has
been suggested that the core components of UIMs
contain 18 amino acid (aa) residues including a core
Ø-XX-Ala-XXX-Ser-XX-Ac (Ø: a large hydrophobic
residue; Ac: an acidic residue), which likely form a short
helix embedded into different protein folds. [33] Ahead of
this core sequence, a short 10-aa peptide may create
specificity to its binding partners. Secondly, the 3D
E F
structure of epsin-UIM may fit the binding to VEGFR2
pockets more suitably than other angiogenic receptor
molecules. Third, tumor cells in general secrete more
VEGF than other angiogenic substances so that
VEGFR2 may have more chances to be activated and
ubiquitylated. Therefore, the epsin-UPI peptide may
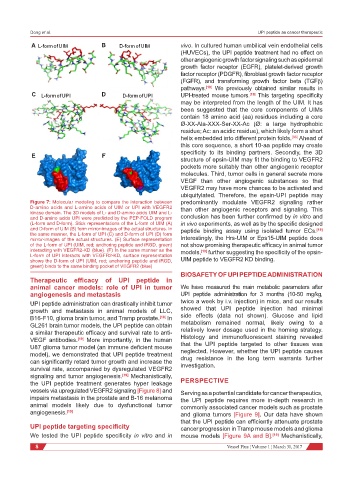
Figure 7: Molecular modeling to compare the interaction between predominantly modulate VEGFR2 signaling rather
D-amino acids and L-amino acids of UIM or UPI with VEGFR2 than other angiogenic receptors and signaling. This
kinase domain. The 3D models of L- and D-amino acids UIM and L-
and D-amino acids UPI were predicted by the PEP-FOLD program conclusion has been further confirmed by in vitro and
(L-form and D-form). Stick representations of the L-form of UIM (A) in vivo experiments, as well as by the specific designed
and D-form of UIM (B) form mirror-images of the actual structures. In peptide binding assay using isolated tumor ECs. [19]
the same manner, the L-form of UPI (C) and D-form of UPI (D) form
mirror-images of the actual structures. (E) Surface representation Interestingly, the Hrs-UIM or Eps15-UIM peptide does
of the L-form of UPI (UIM, red; anchoring peptide and iRGD, green) not show promising therapeutic efficacy in animal tumor
interacting with VEGFR2-KD (blue). (F) In the same manner as the models, [19] further suggesting the specificity of the epsin-
L-form of UPI interacts with VEGFR2-KD, surface representation
shows the D-form of UPI (UIM, red; anchoring peptide and iRGD, UIM peptide to VEGFR2 KD binding.
green) binds to the same binding pocket of VEGFR2 (blue)
BIOSAFETY OF UPI PEPTIDE ADMINISTRATION
Therapeutic efficacy of UPI peptide in
animal cancer models: role of UPI in tumor We have measured the main metabolic parameters after
angiogenesis and metastasis UPI peptide administration for 3 months (10-50 mg/kg,
UPI peptide administration can drastically inhibit tumor twice a week by i.v. injection) in mice, and our results
growth and metastasis in animal models of LLC, showed that UPI peptide injection had minimal
B16-F10, glioma brain tumor, and Tramp prostate. [19] In side effects (data not shown). Glucose and lipid
GL261 brain tumor models, the UPI peptide can obtain metabolism remained normal, likely owing to a
a similar therapeutic efficacy and survival rate to anti- relatively lower dosage used in the homing strategy.
VEGF antibodies. [19] More importantly, in the human Histology and immunofluorescent staining revealed
U87 glioma tumor model (an immune deficient mouse that the UPI peptide targeted to other tissues was
neglected. However, whether the UPI peptide causes
model), we demonstrated that UPI peptide treatment drug resistance in the long term warrants further
can significantly retard tumor growth and increase the investigation.
survival rate, accompanied by dysregulated VEGFR2
signaling and tumor angiogenesis. [19] Mechanistically,
the UPI peptide treatment generates hyper leakage PERSPECTIVE
vessels via upregulated VEGFR2 signaling [Figure 8] and Serving as a potential candidate for cancer therapeutics,
impairs metastasis in the prostate and B-16 melanoma the UPI peptide requires more in-depth research in
animal models likely due to dysfunctional tumor commonly associated cancer models such as prostate
angiogenesis. [19] and glioma tumors [Figure 9]. Our data have shown
that the UPI peptide can efficiently attenuate prostate
UPI peptide targeting specificity cancer progression in Tramp mouse models and glioma
We tested the UPI peptide specificity in vitro and in mouse models [Figure 9A and B]. [19] Mechanistically,
8 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017