Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
Dong et al. UPI peptide as cancer therapeutic
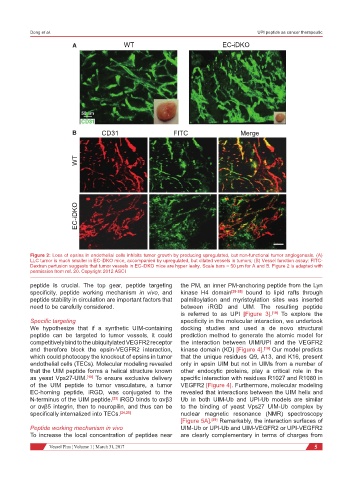
A WT EC-iDKO
B CD31 FITC Merge
WT
EC-iDKO
Figure 2: Loss of epsins in endothelial cells inhibits tumor growth by producing upregulated, but non-functional tumor angiogenesis. (A)
LLC tumor is much smaller in EC-iDKO mice, accompanied by upregulated, but dilated vessels in tumors; (B) Vessel function assay: FITC-
Dextran perfusion suggests that tumor vessels in EC-iDKO mice are hyper leaky. Scale bars = 50 µm for A and B. Figure 2 is adapted with
permission from ref. 20. Copyright 2012 ASCI
peptide is crucial. The top gear, peptide targeting the PM, an inner PM-anchoring peptide from the Lyn
specificity, peptide working mechanism in vivo, and kinase H4 domain [26-28] bound to lipid rafts through
peptide stability in circulation are important factors that palmitoylation and myristoylation sites was inserted
need to be carefully considered. between iRGD and UIM. The resulting peptide
is referred to as UPI [Figure 3]. [19] To explore the
Specific targeting specificity in the molecular interaction, we undertook
We hypothesize that if a synthetic UIM-containing docking studies and used a de novo structural
peptide can be targeted to tumor vessels, it could prediction method to generate the atomic model for
competitively bind to the ubiquitylated VEGFR2 receptor the interaction between UIM/UPI and the VEGFR2
and therefore block the epsin-VEGFR2 interaction, kinase domain (KD) [Figure 4]. [19] Our model predicts
which could photocopy the knockout of epsins in tumor that the unique residues Q9, A13, and K16, present
endothelial cells (TECs). Molecular modeling revealed only in epsin UIM but not in UIMs from a number of
that the UIM peptide forms a helical structure known other endocytic proteins, play a critical role in the
as yeast Vps27-UIM. [19] To ensure exclusive delivery specific interaction with residues R1027 and R1080 in
of the UIM peptide to tumor vasculature, a tumor VEGFR2 [Figure 4]. Furthermore, molecular modeling
EC-homing peptide, iRGD, was conjugated to the revealed that interactions between the UIM helix and
N-terminus of the UIM peptide. [23] iRGD binds to αvβ3 Ub in both UIM-Ub and UPI-Ub models are similar
or αvβ5 integrin, then to neuropilin, and thus can be to the binding of yeast Vps27 UIM-Ub complex by
specifically internalized into TECs. [24,25] nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
[Figure 5A]. [29] Remarkably, the interaction surfaces of
Peptide working mechanism in vivo UIM-Ub or UPI-Ub and UIM-VEGFR2 or UPI-VEGFR2
To increase the local concentration of peptides near are clearly complementary in terms of charges from
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017 5