Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Dong et al. UPI peptide as cancer therapeutic
INTRODUCTION
Angiogenesis is essential for embryogenesis and
postnatal tissue repair. Deadly cancers, however,
can emerge from tumor angiogenesis, a physiological
process involving the production of functional vessels
for cancer cell embedment, colonization, growth,
and metastasis. In 1971, Folkman hypothesized
[1]
that inhibition of tumor angiogenesis is a potentially
powerful tool for cancer therapy. [2-6] With the
identification of more and more new molecules
modulating angiogenesis, [6-8] targeting tumor
angiogenesis has become increasingly likely, and the
concept of inhibiting tumor vessel growth has led to the
discovery of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
and the anti-VEGF antibody, Bevacizumab (Avastin).
Bevacizumab is an angiogenic inhibitor approved by
the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for certain
metastatic cancers such as colorectal cancer and lung
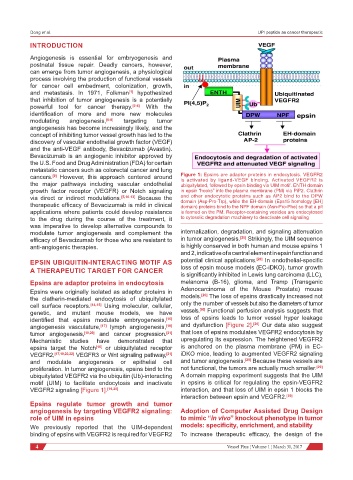
cancers. However, this approach centered around Figure 1: Epsins are adaptor proteins in endocytosis. VEGFR2
[9]
is activated by ligand-VEGF binding. Activated VEGFR2 is
the major pathways including vascular endothelial ubiquitylated, followed by epsin binding via UIM motif. ENTH domain
growth factor receptor (VEGFR) or Notch signaling in epsin “hooks” into the plasma membrane (PM) via PiP2. Clathrin
via direct or indirect modulations. [5,10-13] Because the and other endocytotic proteins such as AP2 bind to the DPW
therapeutic efficacy of Bevacizumab is mild in clinical domain (Asp-Pro-Trp), while the EH-domain (Eps15 homology [EH]
domain) proteins bind to the NPF domain (Asn-Pro-Phe) so that a pit
applications where patients could develop resistance is formed on the PM. Receptor-containing vesicles are endocytosed
to the drug during the course of the treatment, it to cytosolic degradation machinery to deactivate cell signaling
was imperative to develop alternative compounds to
modulate tumor angiogenesis and complement the internalization, degradation, and signaling attenuation
efficacy of Bevacizumab for those who are resistant to in tumor angiogenesis. [20] Strikingly, the UIM sequence
anti-angiogenic therapies. is highly conserved in both human and mouse epsins 1
and 2, indicative of a central element in epsin function and
EPSIN UBIQUITIN-INTERACTING MOTIF AS potential clinical applications. [20] In endothelial-specific
A THERAPEUTIC TARGET FOR CANCER loss of epsin mouse models (EC-iDKO), tumor growth
is significantly inhibited in Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC),
Epsins are adaptor proteins in endocytosis melanoma (B-16), glioma, and Tramp (Transgenic
Epsins were originally isolated as adaptor proteins in Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate) mouse
the clatherin-mediated endocytosis of ubiquitylated models. [20] The loss of epsins drastically increased not
cell surface receptors. [14,15] Using molecular, cellular, only the number of vessels but also the diameters of tumor
[20]
genetic, and mutant mouse models, we have vessels. Functional perfusion analysis suggests that
identified that epsins modulate embryogenesis, [16] loss of epsins leads to tumor vessel hyper leakage
angiogenesis vasculature, [17] lymph angiogenesis, [18] and dysfunction [Figure 2]. [20] Our data also suggest
tumor angiogenesis, [19,20] and cancer progression. that loss of epsins modulates VEGFR2 endocytosis by
[21]
Mechanistic studies have demonstrated that upregulating its expression. The heightened VEGFR2
epsins target the Notch [16] or ubiquitylated receptor is anchored on the plasma membrane (PM) in EC-
VEGFR2, [17,19,20,22] VEGFR3 or Wnt signaling pathway, iDKO mice, leading to augmented VEGFR2 signaling
[21]
and modulate angiogenesis or epithelial cell and tumor angiogenesis. [20] Because these vessels are
proliferation. In tumor angiogenesis, epsins bind to the not functional, the tumors are actually much smaller. [20]
ubiquitylated VEGFR2 via the ubiquitin (Ub)-interacting A domain mapping experiment suggests that the UIM
motif (UIM) to facilitate endocytosis and inactivate in epsins is critical for regulating the epsin-VEGFR2
VEGFR2 signaling [Figure 1]. [19,20] interaction, and that loss of UIM in epsin 1 blocks the
interaction between epsin and VEGFR2. [20]
Epsins regulate tumor growth and tumor
angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR2 signaling: Adoption of Computer Assisted Drug Design
role of UIM in epsins to mimic “in vivo” knockout phenotype in tumor
We previously reported that the UIM-dependent models: specificity, enrichment, and stability
binding of epsins with VEGFR2 is required for VEGFR2 To increase therapeutic efficacy, the design of the
4 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017