Page 100 - Read Online
P. 100
Harangi et al. LDL apheresis or PCSK9 inhibition, or both?
treatments in the Extracorporeal Organ Replacement biweekly, subcutaneously in a dose of 140 mg/day.
Center of University of Debrecen using the Direct After two months of combined apheresis plus PCSK9
Adsorption of Lipoproteins (DALI) system (Fresenius inhibitor treatments we detected further significant
Medical Care). The DALI system can remove ApoB reductions in total cholesterol and LDL-C levels (62.1%
containing lipoproteins from the whole blood in one and 66.1%, respectively), and finally, we achieved
step without prior plasma separation. We used DALI the lipid goals. Hoping that the PCSK9 inhibitor
750 columns, 1:20 proportioned ACD-A (citrate treatment would be effective without further apheresis
solution) for anticoagulation. Average treated volume treatments, we stopped the apheresis and continued
was 8,058 mL/treatment. The total cholesterol, LDL-C the evolocumab therapy. Unfortunately, despite the
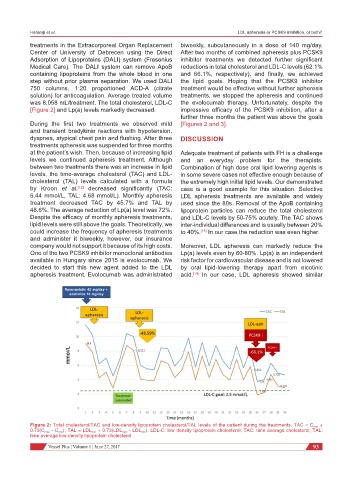
[Figure 2] and Lp(a) levels markedly decreased. impressive efficacy of the PCSK9 inhibition, after a
further three months the patient was above the goals
During the first two treatments we observed mild [Figures 2 and 3].
and transient bradykinin reactions with hypotension,
dyspnea, atypical chest pain and flushing. After three DISCUSSION
treatments apheresis was suspended for three months
at the patient’s wish. Then, because of increasing lipid Adequate treatment of patients with FH is a challenge
levels we continued apheresis treatment. Although and an everyday problem for the therapists.
between two treatments there was an increase in lipid Combination of high dose oral lipid lowering agents is
levels, the time-average cholesterol (TAC) and LDL- in some severe cases not effective enough because of
cholesterol (TAL) levels calculated with a formula the extremely high initial lipid levels. Our demonstrated
by Kroon et al. [12] decreased significantly (TAC: case is a good example for this situation. Selective
6.44 mmol/L, TAL: 4.68 mmol/L). Monthly apheresis LDL apheresis treatments are available and widely
treatment decreased TAC by 45.7% and TAL by used since the 80s. Removal of the ApoB containing
48.6%. The average reduction of Lp(a) level was 72%. lipoprotein particles can reduce the total cholesterol
Despite the efficacy of monthly apheresis treatments, and LDL-C levels by 50-75% acutely. The TAC shows
lipid levels were still above the goals. Theoretically, we inter-individual differences and is usually between 20%
could increase the frequency of apheresis treatments to 40%. In our case the reduction was even higher.
[13]
and administer it biweekly, however, our insurance
company would not support it because of its high costs. Moreover, LDL apheresis can markedly reduce the
One of the two PCSK9 inhibitor monoclonal antibodies Lp(a) levels even by 60-80%. Lp(a) is an independent
available in Hungary since 2015 is evolocumab. We risk factor for cardiovascular disease and is not lowered
decided to start this new agent added to the LDL by oral lipid-lowering therapy apart from nicotinic
apheresis treatment. Evolocumab was administrated acid. In our case, LDL apheresis showed similar
[14]
Figure 2: Total cholesterol/TAC and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/TAL levels of the patient during the treatments. TAC = C min +
0.73(C max - C min ); TAL = LDL min + 0.73(LDL max - LDL min ). LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TAC: time average cholesterol; TAL:
time average low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 27, 2017 93