Page 101 - Read Online
P. 101
Harangi et al. LDL apheresis or PCSK9 inhibition, or both?
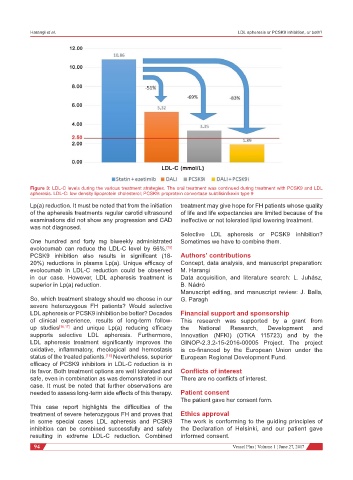
Figure 3: LDL-C levels during the various treatment strategies. The oral treatment was continued during treatment with PCSK9 and LDL
apheresis. LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; PCSK9: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9
Lp(a) reduction. It must be noted that from the initiation treatment may give hope for FH patients whose quality
of the apheresis treatments regular carotid ultrasound of life and life expectancies are limited because of the
examinations did not show any progression and CAD ineffective or not tolerated lipid lowering treatment.
was not diagnosed.
Selective LDL apheresis or PCSK9 inhibition?
One hundred and forty mg biweekly administrated Sometimes we have to combine them.
evolocumab can reduce the LDL-C level by 66%.
[15]
PCSK9 inhibition also results in significant (18- Authors’ contributions
20%) reductions in plasma Lp(a). Unique efficacy of Concept, data analysis, and manuscript preparation:
evolocumab in LDL-C reduction could be observed M. Harangi
in our case. However, LDL apheresis treatment is Data acquisition, and literature search: L. Juhász,
superior in Lp(a) reduction. B. Nádró
Manuscript editing, and manuscript review: J. Balla,
So, which treatment strategy should we choose in our G. Paragh
severe heterozygous FH patients? Would selective
LDL apheresis or PCSK9 inhibition be better? Decades Financial support and sponsorship
of clinical experience, results of long-term follow- This research was supported by a grant from
up studies [16,17] and unique Lp(a) reducing efficacy the National Research, Development and
supports selective LDL apheresis. Furthermore, Innovation (NFKI) (OTKA 115723) and by the
LDL apheresis treatment significantly improves the GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00005 Project. The project
oxidative, inflammatory, rheological and hemostasis is co-financed by the European Union under the
status of the treated patients. Nevertheless, superior European Regional Development Fund.
[18]
efficacy of PCSK9 inhibitors in LDL-C reduction is in
its favor. Both treatment options are well tolerated and Conflicts of interest
safe, even in combination as was demonstrated in our There are no conflicts of interest.
case. It must be noted that further observations are
needed to assess long-term side effects of this therapy. Patient consent
The patient gave her consent form.
This case report highlights the difficulties of the
treatment of severe heterozygous FH and proves that Ethics approval
in some special cases LDL apheresis and PCSK9 The work is conforming to the guiding principles of
inhibition can be combined successfully and safely the Declaration of Helsinki, and our patient gave
resulting in extreme LDL-C reduction. Combined informed consent.
94 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 27, 2017