Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Liu et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.69 Page 11 of 25
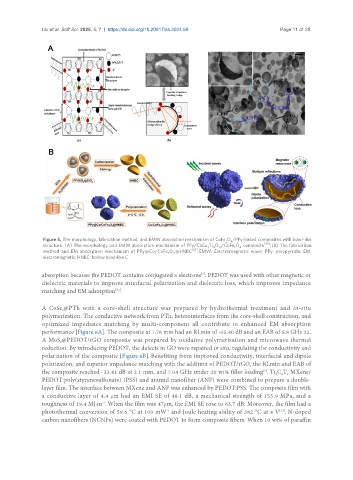
Figure 5. The morphology, fabrication method, and EMW absorption mechanism of CoFe O /PPy-based composites with bowl-like
2
4
structure. (A) The morphology and EMW absorption mechanism of PPy/CaCu Ti O /CoFe O composite [40] ; (B) The fabrication
12
2
3
4
4
method and EM absorption mechanism of PPy@Co/CoFe O @HNBC [63] . EMW: Electromagnetic wave; PPy: polypyrrole; EM:
4
2
electromagnetic; HNBC: hollow bowl-like C.
[7]
absorption because the PEDOT contains conjugated π electrons . PEDOT was used with other magnetic or
dielectric materials to improve interfacial polarization and dielectric loss, which improves impedance
matching and EM adsorption .
[83]
A CoSe @PTh with a core-shell structure was prepared by hydrothermal treatment and in-situ
2
polymerization. The conductive network from PTh, heterointerfaces from the core-shell construction, and
optimized impedance matching by multi-component all contribute to enhanced EM absorption
performance [Figure 6A]. The composite at 1.76 mm had an RLmin of -55.40 dB and an EAB of 5.8 GHz 22.
A MoS @PEDOT/rGO composite was prepared by oxidative polymerization and microwave thermal
2
reduction. By introducing PEDOT, the defects in GO were repaired in situ, regulating the conductivity and
polarization of the composite [Figure 6B]. Benefiting from improved conductivity, interfacial and dipole
polarization, and superior impedance matching with the addition of PEDOT/rGO, the RLmin and EAB of
the composite reached -32.41 dB at 2.1 mm, and 7.04 GHz under 20 wt% filler loading . Ti C T MXene/
[7]
2 x
3
PEDOT:poly(styrenesulfonate) (PSS) and aramid nanofiber (ANF) were combined to prepare a double-
layer film. The interface between MXene and ANF was enhanced by PEDOT:PSS. The composite film with
a conductive layer of 4.4 μm had an EMI SE of 48.1 dB, a mechanical strength of 155.9 MPa, and a
toughness of 19.4 MJ·m . When the film was 47μm, the EMI SE rose to 63.7 dB. Moreover, the film had a
-3
[22]
-2
photothermal conversion of 59.6 °C at 100 mW and Joule heating ability of 382 °C at 4 V . N-doped
carbon nanofibers (NCNFs) were coated with PEDOT to form composite fibers. When 10 wt% of paraffin