Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Page 16 of 25 Liu et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.69
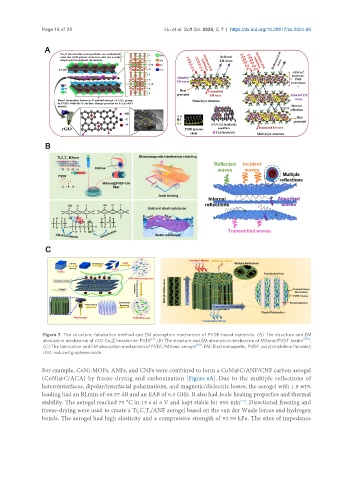
Figure 7. The structure, fabrication method and EM absorption mechanism of PVDF-based materials. (A) The structure and EM
[2]
absorption mechanism of rGO-Co Z hexaferrite-PVDF ; (B) The structure and EM absorption mechanism of MXene/PVDF textile [100] ;
2
(C) The fabrication and EM absorption mechanism of PVDF/MXene aerogel [101] . EM: Electromagnetic; PVDF: poly(vinylidene fluoride);
rGO: reduced graphene oxide.
For example, CoNi-MOFs, ANFs, and CNFs were combined to form a CoNi@C/ANF/CNF carbon aerogel
(CoNi@C/ACA) by freeze-drying and carbonization [Figure 8A]. Due to the multiple reflections of
heterointerfaces, dipolar/interfacial polarizations, and magnetic/dielectric losses, the aerogel with 1.8 wt%
loading had an RLmin of-66.57 dB and an EAB of 6.3 GHz. It also had Joule heating properties and thermal
[14]
stability. The aerogel reached 75 °C in 15 s at 6 V and kept stable for 600 min . Directional freezing and
freeze-drying were used to create a Ti C T /ANF aerogel based on the van der Waals forces and hydrogen
2 x
3
bonds. The aerogel had high elasticity and a compressive strength of 93.59 kPa. The sites of impedance