Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Liu et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.69 Page 17 of 25
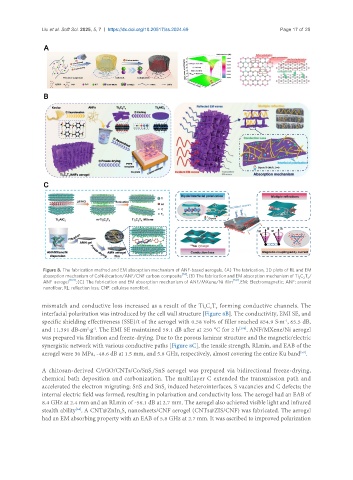
Figure 8. The fabrication method and EM absorption mechanism of ANF-based aerogels. (A) The fabrication, 3D plots of RL and EM
absorption mechanism of CoNi@carbon/ANF/CNF carbon composite [14] ; (B) The fabrication and EM absorption mechanism of Ti C T /
3
2 x
ANF aerogel [104] ; (C) The fabrication and EM absorption mechanism of ANF/MXene/Ni film [50] . EM: Electromagnetic; ANF: aramid
nanofiber; RL: reflection loss; CNF: cellulose nanofibril.
mismatch and conductive loss increased as a result of the Ti C T forming conductive channels. The
3
2 x
interfacial polarization was introduced by the cell wall structure [Figure 8B]. The conductivity, EMI SE, and
specific shielding effectiveness (SSE)/t of the aerogel with 0.58 vol% of filler reached 854.9 S·m , 65.5 dB,
-1
and 11,391 dB·cm ·g . The EMI SE maintained 59.1 dB after at 250 °C for 2 h . ANF/MXene/Ni aerogel
[104]
2
-1
was prepared via filtration and freeze-drying. Due to the porous laminar structure and the magnetic/electric
synergistic network with various conductive paths [Figure 8C], the tensile strength, RLmin, and EAB of the
aerogel were 30 MPa, -48.6 dB at 1.5 mm, and 5.8 GHz, respectively, almost covering the entire Ku band .
[50]
A chitosan-derived C/rGO/CNTs/Co/SnS /SnS aerogel was prepared via bidirectional freeze-drying,
2
chemical bath deposition and carbonization. The multilayer C extended the transmission path and
accelerated the electron migrating; SnS and SnS induced heterointerfaces, S vacancies and C defects; the
2
internal electric field was formed, resulting in polarization and conductivity loss. The aerogel had an EAB of
8.4 GHz at 2.4 mm and an RLmin of -56.1 dB at 2.7 mm. The aerogel also achieved visible light and infrared
stealth ability . A CNT@ZnIn S nanosheets/CNF aerogel (CNTs@ZIS/CNF) was fabricated. The aerogel
[64]
2 4
had an EM absorbing property with an EAB of 5.8 GHz at 2.7 mm. It was ascribed to improved polarization