Page 33 - Read Online
P. 33
Liu et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.69 Page 7 of 25
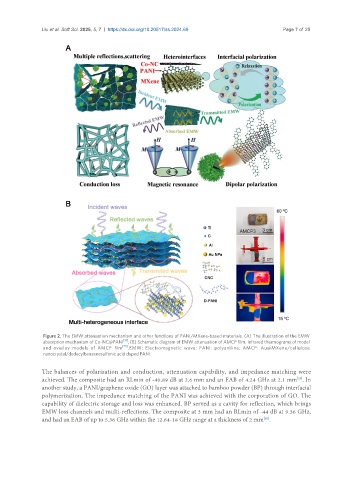
Figure 2. The EMW attenuation mechanism and other functions of PANI/MXene-based materials. (A) The illustration of the EMW
absorption mechanism of Co-NC@PANI [31] ; (B) Schematic diagram of EMW attenuation of AMCP film. Infrared thermograms of model
and overlay models of AMCP film [73] . EMW: Electromagnetic wave; PANI: polyaniline; AMCP: Au@MXene/cellulose
nanocrystal/dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid doped PANI.
The balances of polarization and conduction, attenuation capability, and impedance matching were
[29]
achieved. The composite had an RLmin of -40.89 dB at 2.6 mm and an EAB of 4.24 GHz at 2.1 mm . In
another study, a PANI/graphene oxide (GO) layer was attached to bamboo powder (BP) through interfacial
polymerization. The impedance matching of the PANI was achieved with the corporation of GO. The
capability of dielectric storage and loss was enhanced. BP served as a cavity for reflection, which brings
EMW loss channels and multi-reflections. The composite at 3 mm had an RLmin of -44 dB at 9.36 GHz,
[82]
and had an EAB of up to 5.36 GHz within the 12.64-18 GHz range at a thickness of 2 mm .