Page 176 - Read Online
P. 176
Wang et al. Soft Sci. 2026, 6, 8 Page 19 of 28
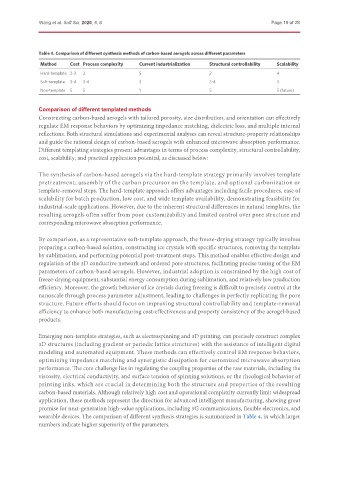
Table 4. Comparison of different synthesis methods of carbon-based aerogels across different parameters
Method Cost Process complexity Current industrialization Structural controllability Scalability
Hard-template 2-3 2 5 2 4
Soft-template 3-4 3-4 3 3-4 3
Non-template 5 5 1 5 5 (future)
Comparison of different templated methods
Constructing carbon-based aerogels with tailored porosity, size distribution, and orientation can effectively
regulate EM response behaviors by optimizing impedance matching, dielectric loss, and multiple internal
reflections. Both structural simulations and experimental analyses can reveal structure-property relationships
and guide the rational design of carbon-based aerogels with enhanced microwave absorption performance.
Different templating strategies present advantages in terms of process complexity, structural controllability,
cost, scalability, and practical application potential, as discussed below:
The synthesis of carbon-based aerogels via the hard-template strategy primarily involves template
pretreatment, assembly of the carbon precursor on the template, and optional carbonization or
template-removal steps. The hard-template approach offers advantages including facile procedures, ease of
scalability for batch production, low cost, and wide template availability, demonstrating feasibility for
industrial-scale applications. However, due to the inherent structural differences in natural templates, the
resulting aerogels often suffer from poor customizability and limited control over pore structure and
corresponding microwave absorption performance.
By comparison, as a representative soft-template approach, the freeze-drying strategy typically involves
preparing a carbon-based solution, constructing ice crystals with specific structures, removing the template
by sublimation, and performing potential post-treatment steps. This method enables effective design and
regulation of the 3D conductive network and ordered pore structures, facilitating precise tuning of the EM
parameters of carbon-based aerogels. However, industrial adoption is constrained by the high cost of
freeze-drying equipment, substantial energy consumption during sublimation, and relatively low production
efficiency. Moreover, the growth behavior of ice crystals during freezing is difficult to precisely control at the
nanoscale through process parameter adjustment, leading to challenges in perfectly replicating the pore
structure. Future efforts should focus on improving structural controllability and template-removal
efficiency to enhance both manufacturing cost-effectiveness and property consistency of the aerogel-based
products.
Emerging non-template strategies, such as electrospinning and 3D printing, can precisely construct complex
3D structures (including gradient or periodic lattice structures) with the assistance of intelligent digital
modeling and automated equipment. These methods can effectively control EM response behaviors,
optimizing impedance matching and synergistic dissipation for customized microwave absorption
performance. The core challenge lies in regulating the coupling properties of the raw materials, including the
viscosity, electrical conductivity, and surface tension of spinning solutions, or the rheological behavior of
printing inks, which are crucial in determining both the structure and properties of the resulting
carbon-based materials. Although relatively high cost and operational complexity currently limit widespread
application, these methods represent the direction for advanced intelligent manufacturing, showing great
promise for next-generation high-value applications, including 5G communications, flexible electronics, and
wearable devices. The comparison of different synthesis strategies is summarized in Table 4, in which larger
numbers indicate higher superiority of the parameters.