Page 125 - Read Online
P. 125
Page 4 of 8 Xiao et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.51
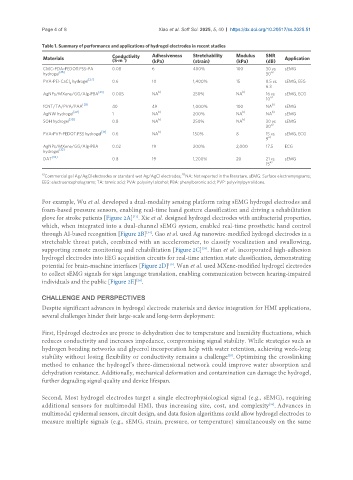
Table 1. Summary of performance and applications of hydrogel electrodes in recent studies
Materials Conductivity Adhesiveness Stretchability Modulus SNR Application
-1
(S·m )
(strain)
(kPa)
(dB)
(kPa)
CMC-PDA-PEDOT:PSS-PA 0.08 6 400% 100 30 vs. sEMG
hydrogel [26] 30 a)
[27]
PVA-PEI-CaCl hydrogel 0.6 10 1,400% 15 8.5 vs. sEMG, EEG
2
6.3
[23] b) b)
AgNPs/MXene/GG/Alg-PBA 0.005 NA 250% NA 16 vs. sEMG, ECG
a)
10
fCNT/TA/PVA/PAA [28] 40 49 1,000% 100 NA b) sEMG
[29] b) b) b)
AgNW hydrogel 1 NA 200% NA NA sEMG
SOH hydrogel [30] 0.8 NA b) 250% NA b) 30 vs. sEMG
a)
30
PVA-PVP-PEDOT:PSS hydrogel [31] 0.6 NA b) 150% 8 15 vs. sEMG, ECG
a)
9
AgNPs/MXene/GG/Alg-PBA 0.02 19 200% 2,000 17.5 ECG
[32]
hydrogel
DAT [33] 0.8 19 1,200% 20 21 vs. sEMG
a)
15
a) b)
Commercial gel Ag/AgCl electrodes or standard wet Ag/AgCl electrodes; NA: Not reported in the literature. sEMG: Surface electromyograms;
EEG: electroencephalograms; TA: tannic acid; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; PBA: phenylboronic acid; PVP: polyvinylpyrrolidone.
For example, Wu et al. developed a dual-modality sensing platform using sEMG hydrogel electrodes and
foam-based pressure sensors, enabling real-time hand gesture classification and driving a rehabilitation
glove for stroke patients [Figure 2A] . Xie et al. designed hydrogel electrodes with antibacterial properties,
[17]
which, when integrated into a dual-channel sEMG system, enabled real-time prosthetic hand control
[34]
through AI-based recognition [Figure 2B] . Gao et al. used Ag nanowire-modified hydrogel electrodes in a
stretchable throat patch, combined with an accelerometer, to classify vocalization and swallowing,
supporting remote monitoring and rehabilitation [Figure 2C] . Han et al. incorporated high-adhesion
[29]
hydrogel electrodes into EEG acquisition circuits for real-time attention state classification, demonstrating
[19]
potential for brain-machine interfaces [Figure 2D] . Wan et al. used MXene-modified hydrogel electrodes
to collect sEMG signals for sign language translation, enabling communication between hearing-impaired
individuals and the public [Figure 2E] .
[24]
CHALLENGE AND PERSPECTIVES
Despite significant advances in hydrogel electrode materials and device integration for HMI applications,
several challenges hinder their large-scale and long-term deployment:
First, Hydrogel electrodes are prone to dehydration due to temperature and humidity fluctuations, which
reduces conductivity and increases impedance, compromising signal stability. While strategies such as
hydrogen bonding networks and glycerol incorporation help with water retention, achieving week-long
stability without losing flexibility or conductivity remains a challenge . Optimizing the crosslinking
[35]
method to enhance the hydrogel’s three-dimensional network could improve water absorption and
dehydration resistance. Additionally, mechanical deformation and contamination can damage the hydrogel,
further degrading signal quality and device lifespan.
Second, Most hydrogel electrodes target a single electrophysiological signal (e.g., sEMG), requiring
additional sensors for multimodal HMI, thus increasing size, cost, and complexity . Advances in
[36]
multimodal epidermal sensors, circuit design, and data fusion algorithms could allow hydrogel electrodes to
measure multiple signals (e.g., sEMG, strain, pressure, or temperature) simultaneously on the same