Page 90 - Read Online
P. 90
Page 14 of 31 Kim et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.28
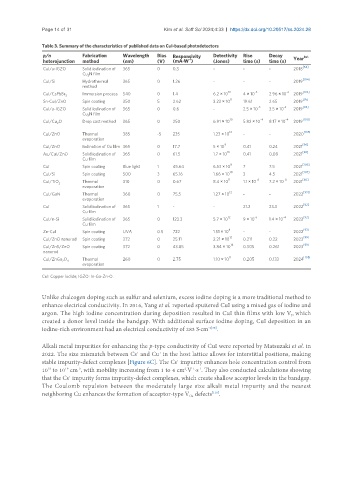
Table 3. Summary of the characteristics of published data on CuI-based photodetectors
p/n Fabrication Wavelength Bias Responsivity Detectivity Rise Decay Year Ref.
-1
heterojunction method (nm) (V) (mA·W ) (Jones) time (s) time (s)
[64]
CuI/a-IGZO Solid iodination of 365 0 0.3 - - - 2018
Cu N film
3
[104]
CuI/Si Hydrothermal 365 0 1.26 - - - 2019
method
10 -5 -2 [103]
CuI/CsPbBr Immersion process 540 0 1.4 6.2 × 10 4 × 10 2.96 × 10 2019
3
11 [95]
Sn-CuI/ZnO Spin coating 350 5 2.62 3.23 × 10 19.61 2.65 2019
CuI/a-IGZO Solid iodination of 365 0 0.6 - 2.5 × 10 -3 3.5 × 10 -2 2019 [94]
Cu N film
3
CuI/Cu O Drop cast method 365 0 250 6.91 × 10 10 5.82 × 10 -4 8.17 × 10 -4 2019 [100]
2
12 [105]
CuI/ZnO Thermal 385 -5 235 1.23 × 10 - - 2020
evaporation
9 [96]
CuI/ZnO Iodination of Cu film 365 0 17.7 5 × 10 0.41 0.24 2021
Au/CuI/ZnO Solid iodination of 365 0 61.5 1.7 × 10 10 0.41 0.08 2021 [96]
Cu film
CuI Spin coating Blue light 1 45.64 6.53 × 10 9 7 7.5 2021 [106]
10 [107]
CuI/Si Spin coating 500 3 65.16 1.66 × 10 3 4.5 2021
11 -4 -4 [60]
CuI/TiO 2 Thermal 310 0 0.67 8.4 × 10 1.1 × 10 7.2 × 10 2021
evaporation
12 [101]
CuI/GaN Thermal 360 0 75.5 1.27 × 10 - - 2022
evaporation
[92]
CuI Solid iodination of 365 1 - - 21.2 23.3 2022
Cu film
12 -5 -4 [92]
CuI/n-Si Solid iodination of 365 0 123.3 5.7 × 10 9 × 10 1.4 × 10 2022
Cu film
8 [93]
Zn-CuI Spin coating UVA 0.5 722 1.51 × 10 - - 2022
12 [99]
CuI/ZnO nanorod Spin coating 372 0 25.11 2.21 × 10 0.211 0.22 2023
CuI/ZnS/ZnO Spin coating 372 0 43.85 3.84 × 10 14 0.305 0.261 2023 [99]
nanorod
CuI/ZnGa O 4 Thermal 260 0 2.75 1.10 × 10 11 0.205 0.133 2024 [108]
2
evaporation
CuI: Copper iodide; IGZO: In-Ga-Zn-O.
Unlike chalcogen doping such as sulfur and selenium, excess iodine doping is a more traditional method to
enhance electrical conductivity. In 2016, Yang et al. reported sputtered CuI using a mixed gas of iodine and
argon. The high iodine concentration during deposition resulted in CuI thin films with low V , which
I
created a donor level inside the bandgap. With additional surface iodine doping, CuI deposition in an
iodine-rich environment had an electrical conductivity of 283 S·cm -1[38] .
Alkali metal impurities for enhancing the p-type conductivity of CuI were reported by Matsuzaki et al. in
2022. The size mismatch between Cs and Cu in the host lattice allows for interstitial positions, making
+
+
+
stable impurity-defect complexes [Figure 6C]. The Cs impurity enhances hole concentration control from
10 to 10 cm , with mobility increasing from 1 to 4 cm ·V ·s . They also conducted calculations showing
-3
2
13
19
-1 -1
that the Cs impurity forms impurity-defect complexes, which create shallow acceptor levels in the bandgap.
+
The Coulomb repulsion between the moderately large size alkali metal impurity and the nearest
neighboring Cu enhances the formation of acceptor-type V defects .
[110]
Cu