Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
Page 12 of 31 Kim et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.28
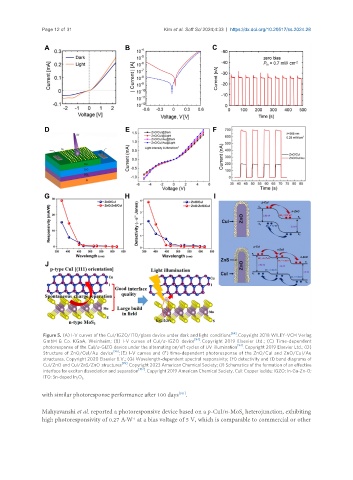
Figure 5. (A) I-V curves of the CuI/IGZO/ITO/glass device under dark and light conditions [64] . Copyright 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag
GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim; (B) I-V curves of CuI/a-IGZO device [94] . Copyright 2019 Elsevier Ltd.; (C) Time-dependent
photoresponse of the CuI/a-GIZO device under the alternating on/off cycles of UV illumination [94] . Copyright 2019 Elsevier Ltd.; (D)
Structure of ZnO/CuI/Au device [96] ; (E) I-V curves and (F) time-dependent photoresponse of the ZnO/CuI and ZnO/CuI/Au
structures. Copyright 2020 Elsevier B.V.; (G) Wavelength-dependent spectral responsivity; (H) detectivity and (I) band diagrams of
CuI/ZnO and CuI/ZnS/ZnO structures [99] . Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society; (J) Schematics of the formation of an effective
interface for exciton dissociation and separation [102] . Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. CuI: Copper iodide; IGZO: In-Ga-Zn-O;
ITO: Sn-doped In O . 3
2
with similar photoresponse performance after 100 days .
[101]
Mahyavanshi et al. reported a photoresponsive device based on a p-CuI/n-MoS heterojunction, exhibiting
2
high photoresponsivity of 0.27 A·W at a bias voltage of 5 V, which is comparable to commercial or other
-1