Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Jin et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:8 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2022.34 Page 9 of 26
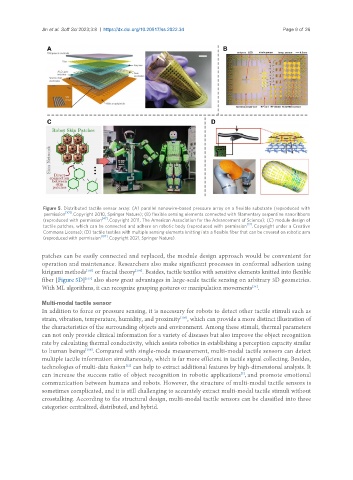
Figure 5. Distributed tactile sensor array: (A) parallel nanowire-based pressure array on a flexible substrate (reproduced with
permission [101] . Copyright 2010, Springer Nature); (B) flexible sensing elements connected with filamentary serpentine nanoribbons
(reproduced with permission [47] . Copyright 2011, The American Association for the Advancement of Science); (C) module design of
tactile patches, which can be connected and adhere on robotic body (reproduced with permission [22] . Copyright under a Creative
Commons License); (D) tactile textiles with multiple sensing elements knitting into a flexible fiber that can be covered on robotic arm
[107]
(reproduced with permission . Copyright 2021, Springer Nature).
patches can be easily connected and replaced, the module design approach would be convenient for
operation and maintenance. Researchers also make significant processes in conformal adhesion using
[105]
[106]
kirigami methods or fractal theory . Besides, tactile textiles with sensitive elements knitted into flexible
fiber [Figure 5D] also show great advantages in large-scale tactile sensing on arbitrary 3D geometries.
[107]
[34]
With ML algorithms, it can recognize grasping gestures or manipulation movements .
Multi-modal tactile sensor
In addition to force or pressure sensing, it is necessary for robots to detect other tactile stimuli such as
strain, vibration, temperature, humidity, and proximity , which can provide a more distinct illustration of
[108]
the characteristics of the surrounding objects and environment. Among these stimuli, thermal parameters
can not only provide clinical information for a variety of diseases but also improve the object recognition
rate by calculating thermal conductivity, which assists robotics in establishing a perception capacity similar
to human beings . Compared with single-mode measurement, multi-modal tactile sensors can detect
[108]
multiple tactile information simultaneously, which is far more efficient in tactile signal collecting. Besides,
technologies of multi-data fusion can help to extract additional features by high-dimensional analysis. It
[12]
can increase the success ratio of object recognition in robotic applications , and promote emotional
[7]
communication between humans and robots. However, the structure of multi-modal tactile sensors is
sometimes complicated, and it is still challenging to accurately extract multi-modal tactile stimuli without
crosstalking. According to the structural design, multi-modal tactile sensors can be classified into three
categories: centralized, distributed, and hybrid.