Page 80 - Read Online
P. 80
Garza de la Llave et al. Syndactyly release with a vascular random pattern flap
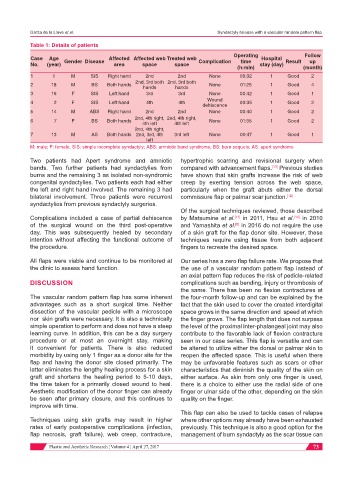
Table 1: Details of patients
Operating Follow
Case Age Gender Disease Affected Affected web Treated web Complication time Hospital Result up
No. (year) area space space stay (day)
(h:min) (month)
1 1 M SIS Right hand 2nd 2nd None 00:32 1 Good 2
2nd, 3rd both 2nd, 3rd both
2 18 M BS Both hands None 01:25 1 Good 4
hands hands
3 16 F SIS Left hand 3rd 3rd None 00:42 1 Good 1
Wound
4 2 F SIS Left hand 4th 4th 00:35 1 Good 2
dehiscence
5 14 M ABS Right hand 2nd 2nd None 00:40 1 Good 2
2nd, 4th right, 2nd, 4th right,
6 7 F BS Both hands None 01:35 1 Good 2
4th left 4th left
2nd, 4th right,
7 13 M AS Both hands 2nd, 3rd, 4th 3rd left None 00:47 1 Good 1
left
M: male; F: female; SIS: simple incomplete syndactyly; ABS: amniotic band syndrome; BS: burn sequels; AS: apert syndrome
Two patients had Apert syndrome and amniotic hypertrophic scarring and revisional surgery when
bands. Two further patients had syndactylies from compared with advancement flaps. Previous studies
[13]
burns and the remaining 3 as isolated non-syndromic have shown that skin grafts increase the risk of web
congenital syndactylies. Two patients each had either creep by exerting tension across the web space,
the left and right hand involved. The remaining 3 had particularly when the graft abuts either the dorsal
bilateral involvement. Three patients were recurrent commissure flap or palmar scar junction. [12]
syndactylies from previous syndactyly surgeries.
Of the surgical techniques reviewed, those described
Complications included a case of partial dehiscence by Matsumine et al. in 2011, Hsu et al. in 2010
[11]
[14]
of the surgical wound on the third post-operative and Yamashita et al. in 2016 do not require the use
[8]
day. This was subsequently healed by secondary of a skin graft for the flap donor site. However, these
intention without affecting the functional outcome of techniques require using tissue from both adjacent
the procedure. fingers to recreate the desired space.
All flaps were viable and continue to be monitored at Our series has a zero flap failure rate. We propose that
the clinic to assess hand function. the use of a vascular random pattern flap instead of
an axial pattern flap reduces the risk of pedicle-related
DISCUSSION complications such as bending, injury or thrombosis of
the same. There has been no flexion contractures at
The vascular random pattern flap has some inherent the four-month follow-up and can be explained by the
advantages such as a short surgical time. Neither fact that the skin used to cover the created interdigital
dissection of the vascular pedicle with a microscope space grows in the same direction and speed at which
nor skin grafts were necessary. It is also a technically the finger grows. The flap length that does not surpass
simple operation to perform and does not have a steep the level of the proximal inter-phalangeal joint may also
learning curve. In addition, this can be a day surgery contribute to the favorable lack of flexion contracture
procedure or at most an overnight stay, making seen in our case series. This flap is versatile and can
it convenient for patients. There is also reduced be altered to utilize either the dorsal or palmar skin to
morbidity by using only 1 finger as a donor site for the reopen the affected space. This is useful when there
flap and having the donor site closed primarily. The may be unfavorable features such as scars or other
latter eliminates the lengthy healing process for a skin characteristics that diminish the quality of the skin on
graft and shortens the healing period to 5-10 days, either surface. As skin from only one finger is used,
the time taken for a primarily closed wound to heal. there is a choice to either use the radial side of one
Aesthetic modification of the donor finger can already finger or ulnar side of the other, depending on the skin
be seen after primary closure, and this continues to quality on the finger.
improve with time.
This flap can also be used to tackle cases of relapse
Techniques using skin grafts may result in higher where other options may already have been exhausted
rates of early postoperative complications (infection, previously. This technique is also a good option for the
flap necrosis, graft failure), web creep, contracture, management of burn syndactyly as the scar tissue can
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ April 27, 2017 73