Page 75 - Read Online
P. 75
Maher et al. Hypospadias: an algorithm for repair
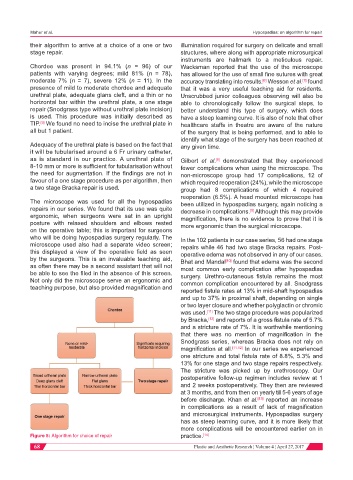
their algorithm to arrive at a choice of a one or two illumination required for surgery on delicate and small
stage repair. structures, where along with appropriate microsurgical
instruments are hallmark to a meticulous repair.
Chordee was present in 94.1% (n = 96) of our Wacksman reported that the use of the microscope
patients with varying degrees; mild 81% (n = 78), has allowed for the use of small fine sutures with great
moderate 7% (n = 7), severe 12% (n = 11). In the accuracy translating into results. Wesson et al. found
[6]
[7]
presence of mild to moderate chordee and adequate that it was a very useful teaching aid for residents.
urethral plate, adequate glans cleft, and a thin or no Unscrubbed junior colleagues observing will also be
horizontal bar within the urethral plate, a one stage able to chronologically follow the surgical steps, to
repair (Snodgrass type without urethral plate incision) better understand this type of surgery, which does
is used. This procedure was initially described as have a steep learning curve. It is also of note that other
TIP. We found no need to incise the urethral plate in healthcare staffs in theatre are aware of the nature
[5]
all but 1 patient. of the surgery that is being performed, and to able to
identify what stage of the surgery has been reached at
Adequacy of the urethral plate is based on the fact that any given time.
it will be tubularised around a 6 Fr urinary catheter,
as is standard in our practice. A urethral plate of Gilbert et al. demonstrated that they experienced
[8]
8-10 mm or more is sufficient for tubularisation without fewer complications when using the microscope. The
the need for augmentation. If the findings are not in non-microscope group had 17 complications, 12 of
favour of a one stage procedure as per algorithm, then which required reoperation (24%), while the microscope
a two stage Bracka repair is used. group had 8 complications of which 4 required
reoperation (6.5%). A head mounted microscope has
The microscope was used for all the hypospadias been utilized in hypospadias surgery, again noticing a
repairs in our series. We found that its use was quite decrease in complications. Although this may provide
[9]
ergonomic, when surgeons were sat in an upright magnification, there is no evidence to prove that it is
posture with relaxed shoulders and elbows rested more ergonomic than the surgical microscope.
on the operative table; this is important for surgeons
who will be doing hypospadias surgery regularly. The In the 102 patients in our case series, 56 had one stage
microscope used also had a separate video screen; repairs while 46 had two stage Bracka repairs. Post-
this displayed a view of the operative field as seen operative edema was not observed in any of our cases.
by the surgeons. This is an invaluable teaching aid, Bhat and Mandal found that edema was the second
[10]
as often there may be a second assistant that will not most common early complication after hypospadias
be able to see the filed in the absence of this screen. surgery. Urethro-cutaneous fistula remains the most
Not only did the microscope serve an ergonomic and common complication encountered by all. Snodgrass
teaching purpose, but also provided magnification and
reported fistula rates at 13% in mid-shaft hypospadias
and up to 37% in proximal shaft, depending on single
or two layer closure and whether polyglactin or chromic
was used. The two stage procedure was popularized
[11]
by Bracka, and reports of a gross fistula rate of 5.7%
[12]
and a stricture rate of 7%. It is worthwhile mentioning
that there was no mention of magnification in the
Snodgrass series, whereas Bracka does not rely on
magnification at all. [11,12] In our series we experienced
one stricture and total fistula rate of 8.8%, 5.3% and
13% for one stage and two stage repairs respectively.
The stricture was picked up by urethroscopy. Our
postoperative follow-up regimen includes review at 1
and 2 weeks postoperatively. They then are reviewed
at 3 months, and from then on yearly till 5-6 years of age
before discharge. Khan et al. reported an increase
[13]
in complications as a result of lack of magnification
and microsurgical instruments. Hypospadias surgery
has as steep learning curve, and it is more likely that
more complications will be encountered earlier on in
Figure 5: Algorithm for choice of repair practice. [14]
68 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ April 27, 2017