Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Garza de la Llave et al. Syndactyly release with a vascular random pattern flap
fall short of the nail fold. or local anesthesia. Pre-operative exsanguination of
the hand is used in all cases and can be achieved with
The goal of treatment is to create a functional an Esmarch bandage or pneumatic device (Kidde).
hand with minimal long-term morbidity. In order to
achieve this, an aesthetically pleasing and functional Creation of the new webspace opening
interdigital space must be created preferably with as Under ×3.5 surgical loupe magnification, the
few procedures as possible. The current techniques syndactylized soft tissue is incised with a 15 blade along
[4]
available are based at the opening of the webspace the previous markings to achieve the desired webspace
with the purpose of obtaining a normal webspace depth [Figure 3]. Blunt dissection of the interdigital
while supplying adequate skin coverage for it. [1,5-7] space is performed with special consideration taken
These surgical techniques can be classified into two to release the natatory ligament and to preserve the
types: those utilizing a local flaps alone and those that digital neurovascular bundles [Figure 4].
use skin grafting in addition to it. The latter technique
is used especially in difficult cases of complete Flap dissection
syndactyly to treat the fusion distal to distal inter- The skin and subcutaneous tissue of the flap is
phalangeal joint. However in mild cases, such as dissected along the pre-marked limits. Distal to proximal
incomplete syndactyly proximal to the proximal inter- dissection is performed with thin curved scissors,
phalangeal joint, various techniques for correcting the achieving adequate flap thickness without damaging
web only with local flaps from surrounding tissues the main vascular pedicle of the finger. Only the skin
have been reported. Some of the techniques used to and the subcutaneous tissue should be raised with the
[8]
recreate the webspaces include split and full-thickness flap and must not include the main vascular pedicle of
skin grafts. Examples of local flaps used are such as the finger. Thus, the flap is of a vascular random pattern
[9]
the dorsal rectangular, palmar rectangular, interposed variety and must not exceed the length to base width
“V”, dorsal metacarpal. The proximally-based dorsal ratio of 3:1 to ensure its vascular viability [Figure 5].
[10]
rectangular flap is most commonly used The main
[11]
complications of corrective surgery are infection, Flap rotation
delayed wound healing, graft loss, flap loss, syndactyly The dissected flap must be able to freely rotate to
relapse and contracture of adjacent fingers. [12]
CASE REPORT
Surgical technique
Marking
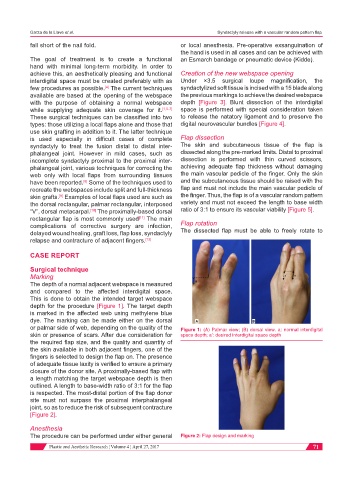
The depth of a normal adjacent webspace is measured
and compared to the affected interdigital space.
This is done to obtain the intended target webspace
depth for the procedure [Figure 1]. The target depth
is marked in the affected web using methylene blue
dye. The marking can be made either on the dorsal
or palmar side of web, depending on the quality of the Figure 1: (A) Palmar view; (B) dorsal view. a: normal interdigital
skin or presence of scars. After due consideration for space depth; a’: desired interdigital space depth
the required flap size, and the quality and quantity of
the skin available in both adjacent fingers, one of the
fingers is selected to design the flap on. The presence
of adequate tissue laxity is verified to ensure a primary
closure of the donor site. A proximally-based flap with
a length matching the target webspace depth is then
outlined. A length to base-width ratio of 3:1 for the flap
is respected. The most-distal portion of the flap donor
site must not surpass the proximal interphalangeal
joint, so as to reduce the risk of subsequent contracture
[Figure 2].
Anesthesia
The procedure can be performed under either general Figure 2: Flap design and marking
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ April 27, 2017 71