Page 108 - Read Online
P. 108
Keren et al. NMR for human fat graft assessment
such as erythropoietin, and growth factors including for non-invasive and sequential ex vivo analysis of
insulin growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, platelet small animals: dual energy X ray absorptiometry
derived growth factor and vascular derived growth (DXA) and small animal NMR. The NMR has several
factor. [23,24] Other relatively new methods include cell- advantages over the DXA including the speed and cost
assisted lipotransfer with adipose-derived stromal of measurements (< 2 min) and the ability to ethically
cells, [25] and the use of an enriched, serum free study non-anesthetized animals. [31,32]
cell culture medium (Cariel) as a supplement to the
injected fat. [18] Although most of these new methods NMR is a physical phenomenon which exploits the
have slightly improved the take of the transplanted magnetic properties of certain nuclei to provide detailed
fat, none have shown truly satisfactory and cost- structural, dynamic and energetic information of
[33]
effective results. molecular compounds. Although NMR spectroscopy
is a powerful technique, application has been limited
The majority of published results on long-term fat due to the high cost and complexity of the device.
survival following transplantation and outcomes Recently, miniaturized low-field benchtop TD-NMR
are based on subjective analysis of photographs or instruments have been developed. While the newly
anecdotal reports. [26,27] In human studies, there is a developed device lacks some degree of sensitivity
relative lack of evidence with only a small number of and resolution, it is capable of powerful relaxation time
objective studies using three-dimensional imaging, analysis and has gained popularity due to its simplicity
ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and and cost-effectiveness.
magnetic resonance imaging. [28-30]
However, validation studies of NMR instruments are
Small animal models have facilitated more accurate currently limited and have not been used in fat graft
evaluations of fat graft survival and “take”. However, assessment. Taicher et al. examined the precision
[34]
histologic assessment of fat grafts in animals is and accuracy of the NMR (EchoMRI) compared to
expensive, time consuming and not amenable to the DXA and chemical carcass analysis. They found
examination of large volumes of tissue and accurate higher precision of NMR (vs. DXA) for measurements
assessment of fat grafted by use of the Coleman of fat content in lean and obese mice. In diet-induced
technique. Further, it requires sacrifice of the animal obese mice, the coefficient of variation for fat mass by
in order for tissues to be harvested for processing, NMR and DXA were 0.34% and 9.59%, respectively.
embedding, sectioning, and staining with subsequent
analytical evaluation. Traditional CT or micro CT In order to overcome the inaccuracy of small droplet
examination is expensive, time consuming (30+ min fat grafting collection and analysis, the use of a whole
per animal), requires anaesthetic, and radiates the body composition analyzer based on NMR technology
animal with roughly 30 Gy. Its use is limited as early fat was studied (Brukersminispec, BCA-Analyzer). It is a
necrosis cannot be easily distinguished from viable fat. precise method for measurement of lean tissue, fat
and fluid in living mice.
Currently, there are two types of instruments available
A useful animal model should resemble the human
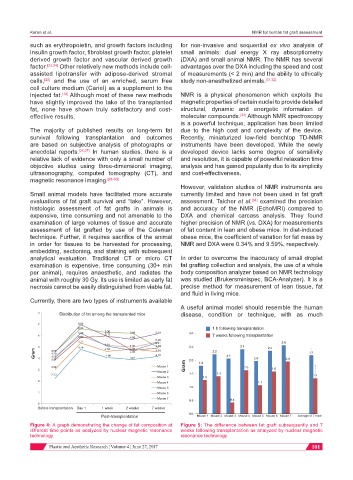
Distribution of fat among the transplanted mice disease, condition or technique, with as much
1 h following transplantation
7 weeks following transplantation
Mouse 1
Mouse 2
Mouse 3
Mouse 4
Mouse 5
Mouse 6
Mouse 7
Before transplantation Day 1 1 week 2 weeks 7 weeks
Post-transplantation Mouse 1 Mouse 2 Mouse 3 Mouse 4 Mouse 5 Mouse 6 Mouse 7 Average of 7 mice
Figure 4: A graph demonstrating the change of fat composition at Figure 5: The difference between fat graft subsequently and 7
different time points as analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance weeks following transplantation as analyzed by nuclear magnetic
technology resonance technology
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ June 27, 2017 101