Page 313 - Read Online
P. 313
Sharma et al. Hard palate cysts
INTRODUCTION
Cysts in the oral cavity can either be of soft tissue origin
or from within the bone. Non-odontogenic hard palate
cysts arise from the tissues which do not participate in
tooth formation. There are many palatal cysts and their
variants are encountered during the course of embryonic
palate development. One of the cysts is globulomaxillary
cyst and this terminology had a lot of dispute to be used.
It was earlier thought to be of embryonic origin because
of entrapment of the ectoderm but now this hypothesis is
no longer considered. These have been considered as
fissural entrapment of epithelium rather than embryonic
ectoderm. There are many other cysts reported in the
[1]
palate region and have been categorized as per the
origin and anatomical location.
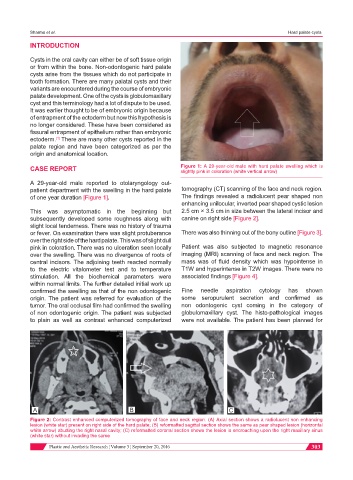
CASE REPORT Figure 1: A 29-year-old male with hard palate swelling which is
slightly pink in coloration (white vertical arrow)
A 29-year-old male reported to otolaryngology out-
patient department with the swelling in the hard palate tomography (CT) scanning of the face and neck region.
of one year duration [Figure 1]. The findings revealed a radiolucent pear shaped non
enhancing unilocular, inverted pear shaped cystic lesion
This was asymptomatic in the beginning but 2.5 cm × 3.5 cm in size between the lateral incisor and
subsequently developed some roughness along with canine on right side [Figure 2].
slight local tenderness. There was no history of trauma
or fever. On examination there was slight protuberance There was also thinning out of the bony outline [Figure 3].
over the right side of the hard palate. This was of slight dull
pink in coloration. There was no ulceration seen locally Patient was also subjected to magnetic resonance
over the swelling. There was no divergence of roots of imaging (MRI) scanning of face and neck region. The
central incisors. The adjoining teeth reacted normally mass was of fluid density which was hypointense in
to the electric vitalometer test and to temperature T1W and hyperintense in T2W images. There were no
stimulation. All the biochemical parameters were associated findings [Figure 4].
within normal limits. The further detailed initial work up
confirmed the swelling as that of the non odontogenic Fine needle aspiration cytology has shown
origin. The patient was referred for evaluation of the some seropurulent secretion and confirmed as
tumor. The oral occlusal film had confirmed the swelling non odontogenic cyst coming in the category of
of non odontogenic origin. The patient was subjected globulomaxillary cyst. The histo-pathological images
to plain as well as contrast enhanced computerized were not available. The patient has been planned for
A B C
Figure 2: Contrast enhanced computerized tomography of face and neck region. (A) Axial section shows a radiolucent non enhancing
lesion (white star) present on right side of the hard palate; (B) reformatted sagittal section shows the same as pear shaped lesion (horizontal
white arrow) abutting the right nasal cavity; (C) reformatted coronal section shows the lesion is encroaching upon the right maxillary sinus
(white star) without invading the same
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 20, 2016 303