Page 302 - Read Online
P. 302
Hwang et al. Medially based de-epithelialized flap
INTRODUCTION the depressed nostril sill.
In patients with cleft lip nasal deformities, the upper lip We performed a histological observation of the nostril
scar is widened and the nasal base is wider than the floor in a gross cadaveric specimen and created a
unaffected side. Alar base reduction is an important medially based de-epithelialized flap for nasal base
technique for narrowing the frontal view of the nose. [1] narrowing and nostril sill augmentation in cleft lip nasal
deformities.
Moreover, the nostril sill is deficient on the affected side.
Excision of the scar of the upper lip and nostril sill may METHODS
leave a depressed nostril. Some authors have used
[2]
laterally based alar flaps, stating that they were able Cadaveric study
[3]
to reduce the risk of notching by adapting a two-layer On a cadaver, the nose including the upper lip was
closure of the vestibular floor. [2] removed and fixed in 4% natural buffered formaldehyde.
A fully thick section was taken from the nostril sill at
We hypothesized that a medially based de-epithelialized the midpoint of the columellar base and the alar base.
flap might avoid the notching of the nostril sill, since the Following routine histologic procedures, the specimens
de-epithelialized part of the excess skin could augment were embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 10 μm, and
stained with Masson trichrome. The prepared slides were
observed under a light microscope. In the perpendicular
A section, the nostril sill was composed of thickened
dermis. Just below the dermis layer, the depressor septi
nasi muscle ran obliquely and augmented the nostril sill.
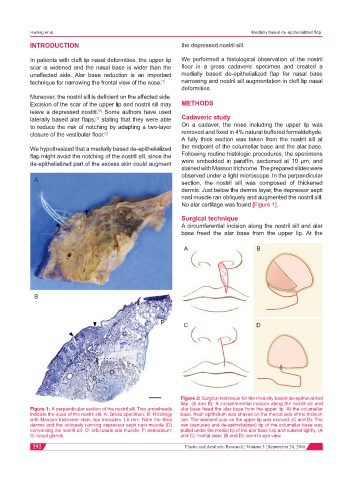
No alar cartilage was found [Figure 1].
Surgical technique
A circumferential incision along the nostril sill and alar
base freed the alar base from the upper lip. At the
A B
B
C D
Figure 2: Surgical technique for the medially based de-epithelialized
flap. (A and B): A circumferential incision along the nostril sill and
Figure 1: A perpendicular section of the nostril sill. Two arrowheads alar base freed the alar base from the upper lip. At the columellar
indicate the span of the nostril sill. A: Gross specimen; B: Histology base, fresh epithelium was shaved on the medial side of the incision
with Masson trichrome stain, bar indicates 1.5 mm. Note the thick line. The widened scar on the upper lip was excised. (C and D): The
dermis and the obliquely running depressor septi nasi muscle (D) raw (denuded and de-epithelialized) tip of the columellar base was
comprising the nostril sill. O: orbicularis oris muscle; P: periosteum; pulled under the medial tip of the alar base flap and sutured tightly. (A
G: nasal glands and C): frontal view; (B and D): worm’s eye view
292 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 20, 2016