Page 33 - Read Online
P. 33
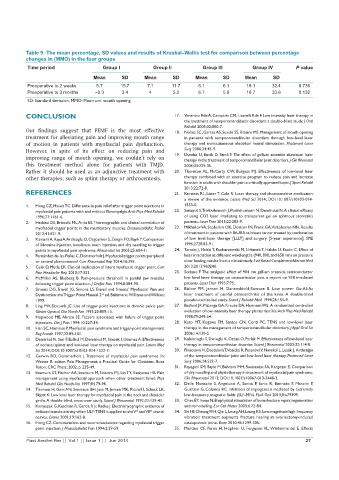
Table 9: The mean percentage, SD values and results of Kruskal–Wallis test for comparison between percentage
changes in (MMO) in the four groups
Time period Group I Group II Group III Group IV P value
Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
Preoperative to 2 weeks 5.7 15.7 7.1 11.7 6.1 6.1 18.1 32.4 0.736
Preoperative to 3 months −0.3 3.4 4 5.2 6.7 5.9 18.7 33.6 0.132
SD: Standard deviation, MMO: Maximum mouth opening
CONCLUSION 17. Venancio Rde A, Camparis CM, Lizarelli Rde F. Low intensity laser therapy in
the treatment of temporomandibular disorders: a double‑blind study. J Oral
Rehabil 2005;32:800‑7.
Our findings suggest that PEMF is the most effective 18. Núñez SC, Garcez AS, Suzuki SS, Ribeiro MS. Management of mouth opening
treatment for alleviating pain and improving mouth range in patients with temporomandibular disorders through low‑level laser
of motion in patients with myofascial pain dysfunction. therapy and transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation. Photomed Laser
However, in spite of its effect on reducing pain and Surg 2006;24:45‑9.
improving range of mouth opening, we couldn’t rely on 19. Dundar U, Eucik D, Samli F. The effect of gallium arsenide aluminum laser
therapy in the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorders. J Clin Rhematol
this treatment method alone for patients with TMJD. 2006;33:229‑35.
Rather it should be used as an adjunctive treatment with 20. Thornton AL, McCarty CW, Burgess MJ. Effectiveness of low‑level laser
other therapies, such as splint therapy or arthrocentesis. therapy combined with an exercise program to reduce pain and increase
function in adults with shoulder pain: a critically appraised topic. J Sport Rehabil
2013;22:72‑8.
REFERENCES 21. Kerstein RL, Lister T, Cole R. Laser therapy and photosensitive medication:
a review of the evidence. Lasers Med Sci 2014; DOI:10.1007/s10103‑014‑
1. Hong CZ, Hsueh TC. Difference in pain relief after trigger point injections in 1553‑0.
myofascial pain patients with and without fibromyalgia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 22. Sattayut S, Trivibulwanich J, Pipithirunkarn N, Danvirutai N. A clinical efficacy
1996;77:1161‑6. of using CO2 laser irradiating to transparent gel on aphthous stomatitis
2. Haddad DS, Brioschi ML, Arita ES. Thermographic and clinical correlation of patients. Laser Ther 2013;22:283‑9.
myofascial trigger points in the masticatory muscles. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 23. Mikhailov VA, Scobelkin OK, Denisov IN, Frank GA, Voltohenko NN. Results
2012;41:621‑9. of treatment in patients with IIA‑III A st. breast cancer treated by combination
3. Kamanli A, Kaya A, Ardicoglu O, Ozgocmen S, Zengin FO, Bayik Y. Comparison of low level laser therapy [LLLT] and surgery [5‑year experience]. SPIE
of lidocaine injection, botulinum toxin injection, and dry needling to trigger 1996;2728:83‑91.
points in myofascial pain syndrome. Rheumatol Int 2005;25:604‑11. 24. Taradaj J, Halski T, Kucharzewski M, Urbanek T, Halska U, Kucio C. Effect of
4. Fernández‑de‑las‑Peñas C, Dommerholt J. Myofascial trigger points: peripheral laser irradiation at different wavelengths (940, 808, and 658 nm) on pressure
or central phenomenon? Curr Rheumatol Rep 2014;16:395. ulcer healing: results from a clinical study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
5. Celik D, Mutlu EK. Clinical implication of latent myofascial trigger point. Curr 2013;2013:960240.
Pain Headache Rep 2013;17:353. 25. Soriano F. The analgesic effect of 904 nm gallium arsenide semiconductor
6. McMillan AS, Blasberg B. Pain‑pressure threshold in painful jaw muscles low level laser therapy on osteoarticular pain, a report on 938 irradiated
following trigger point injection. J Orofac Pain 1994;8:384‑90. patients. Laser Ther 1995;7:75.
7. Simons DG, Travell JG, Simons LS. Travell and Simons’ Myofascial Pain and 26. Bülow PM, Jensen H, Danneskiold‑Samsøe B. Low power Ga‑Al‑As
Dysfunction: the Trigger Point Manual. 2 ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; laser treatment of painful osteoarthritis of the knee. A double‑blind
nd
1999. placebo‑controlled study. Scand J Rehabil Med 1994;26:155‑9.
8. Ling FW, Slocumb JC. Use of trigger point injections in chronic pelvic pain. 27. Basford JR, Malanga GA, Krause DA, Harmsen WS. A randomized controlled
Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 1993;20:809‑15. evaluation of low‑intensity laser therapy: plantar fasciitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil
9. Hopwood MB, Abram SE. Factors associated with failure of trigger point 1998;79:249‑54.
injections. Clin J Pain 1994;10:227‑34. 28. Kato MT, Kogawa EM, Santos CN, Conti PC. TENS and low‑level laser
10. Han SC, Harrison P. Myofascial pain syndrome and trigger‑point management. therapy in the management of temporomandibular disorders. J Appl Oral Sci
Reg Anesth 1997;22:89‑101. 2006;14:130‑5.
11. Demirkol N, Sari F, Bulbul M, Demirkol M, Simsek I, Usumez A. Effectiveness 29. Kulekcioglu S, Sivrioglu K, Ozcan O, Parlak M. Effectiveness of low‑level laser
of occlusal splints and low‑level laser therapy on myofascial pain. Lasers Med therapy in temporomandibular disorder. Scand J Rheumatol 2003;32:114‑8.
Sci 2014; DOI:10.1007/s10103‑014‑1522‑7. 30. Fikácková H, Dostálová T, Vosická R, Peterová V, Navrátil L, Lesák J. Arthralgia
12. Gerwin RD, Dommerholt J. Treatment of myofascial pain syndromes. In: of the temporomandibular joint and low‑level laser therapy. Photomed Laser
Weiner R, editor. Pain Management; a Practical Guide for Clinicians. Boca Surg 2006;24:522‑7.
Raton: CRC Press; 2002. p. 235‑49. 31. Rayegani SM, Bayat M, Bahrami MH, Raeissadat SA, Kargozar E. Comparison
13. Imamura ST, Fischer AA, Imamura M, Teixeira MJ, Lin TY, Kaziyama HS. Pain of dry needling and physiotherapy in treatment of myofascial pain syndrome.
management using myofascial approach when other treatment failed. Phys Clin Rheumatol 2013; DOI:10.1007/s10067‑013‑2448‑3.
Med Rehabil Clin North Am 1997;8:179‑96. 32. Delle Monache S, Angelucci A, Sanità P, Iorio R, Bennato F, Mancini F,
14. Thorsen H, Gam AN, Svensson BH, Jess M, Jensen MK, Piculell I, Schack LK, Gualtieri G, Colonna RC. Inhibition of angiogenesis mediated by extremely
Skjøtt K. Low level laser therapy for myofascial pain in the neck and shoulder low‑frequency magnetic fields (ELF‑MFs). PLoS One 2013;8:e79309.
girdle. A double‑blind, cross‑over study. Scand J Rheumatol 1992;21:139‑41. 33. Chao EY, Inoue N. Biophysical stimulation of bone fracture repair, regeneration
15. Kamyszek G, Ketcham R, Garcia R Jr, Radke J. Electromyographic evidence of and remodelling. Eur Cell Mater 2003;6:72‑84.
reduced muscle activity when ULF‑TENS is applied to the V and VII cranial 34. Shi HF, Cheung WH, Qin L, Leung AH, Leung KS. Low‑magnitude high‑frequency
th
th
nerves. Cranio 2001;19:162‑8. vibration treatment augments fracture healing in ovariectomy‑induced
16. Hong CZ. Considerations and recommendations regarding myofascial trigger osteoporotic bone. Bone 2010;46:1299‑305.
point injection. J Musculoskelet Pain 1994;2:29‑59. 35. Martino CF, Perea H, Hopfner U, Ferguson VL, Wintermantel E. Effects
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 1 || Jun 2014 27