Page 32 - Read Online
P. 32
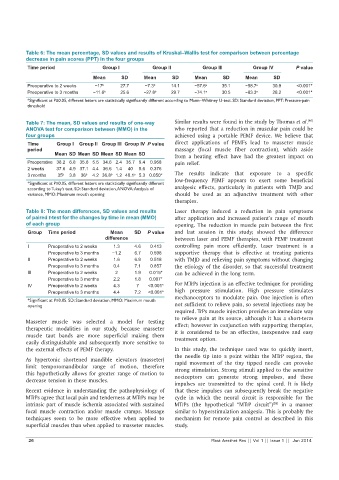
Table 6: The mean percentage, SD values and results of Kruskal–Wallis test for comparison between percentage
decrease in pain scores (PPT) in the four groups
Time period Group I Group II Group III Group IV P value
Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD
Preoperative to 2 weeks −17 b 27.7 −7.3 b 14.1 −57.6 a 35.1 −58.7 a 30.9 <0.001*
Preoperative to 3 months −11.6 b 25.6 −27.8 b 29.7 −74.1 a 30.5 −83.3 a 28.2 <0.001*
*Significant at P≤0.05, different letters are statistically significantly different according to Mann–Whitney U‑test. SD: Standard deviation, PPT: Pressure‑pain
threshold
[40]
Table 7: The mean, SD values and results of one-way Similar results were found in the study by Thomas et al.
ANOVA test for comparison between (MMO) in the who reported that a reduction in muscular pain could be
four groups achieved using a portable PEMF device. We believe that
Time Group I Group II Group III Group IV P value direct applications of PEMFs lead to masseter muscle
period massage (focal muscle fiber contraction), which aside
Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD from a heating effect have had the greatest impact on
Preoperative 36.2 6.8 35.6 5.5 34.6 2.4 35.7 9.4 0.958 pain relief.
2 weeks 37.6 4.9 37.1 4.4 36.6 1.4 40 5.6 0.376
3 months 35 b 3.8 36 b 4.2 36.8 b 1.2 40.1 a 5.3 0.050* The results indicate that exposure to a specific
low-frequency PEMF appears to exert some beneficial
*Significant at P≤0.05, different letters are statistically significantly different
according to Tukey’s test. SD: Standard deviation, ANOVA: Analysis of analgesic effects, particularly in patients with TMJD and
variance, MMO: Maximum mouth opening should be used as an adjunctive treatment with other
therapies.
Table 8: The mean differences, SD values and results Laser therapy induced a reduction in pain symptoms
of paired t-test for the changes by time in mean (MMO) after application and increased patient’s range of mouth
of each group opening. The reduction in muscle pain between the first
Group Time period Mean SD P value and last session in this study; showed the difference
difference between laser and PEMF therapies, with PEMF treatment
I Preoperative to 2 weeks 1.3 4.6 0.413 controlling pain more efficiently. Laser treatment is a
Preoperative to 3 months −1.2 6.7 0.598 supportive therapy that is effective at treating patients
II Preoperative to 2 weeks 1.6 6.9 0.518 with TMJD and relieving pain symptoms without changing
Preoperative to 3 months 0.4 7.1 0.857 the etiology of the disorder, so that successful treatment
III Preoperative to 2 weeks 2 1.9 0.015* can be achieved in the long term.
Preoperative to 3 months 2.2 1.8 0.007*
IV Preoperative to 2 weeks 4.3 7 <0.001* For MTrPs injection is an effective technique for providing
Preoperative to 3 months 4.4 7.2 <0.001* high pressure stimulation. High pressure stimulates
mechanoceptors to modulate pain. One injection is often
*Significant at P≤0.05. SD: Standard deviation, MMO: Maximum mouth
opening not sufficient to relieve pain, so several injections may be
required. TrPs muscle injection provides an immediate way
to relieve pain at its source, although it has a short-term
Masseter muscle was selected a model for testing effect; however in conjunction with supporting therapies,
therapeutic modalities in our study, because masseter
muscle taut bands are more superficial making them it is considered to be an effective, inexpensive and easy
treatment option.
easily distinguishable and subsequently more sensitive to
the external effects of PEMF therapy. In this study, the technique used was to quickly insert,
the needle tip into a point within the MTrP region, the
As hypertonic shortened mandible elevators (masseter) rapid movement of the tiny tipped needle can provoke
limit temporomandibular range of motion, therefore strong stimulation. Strong stimuli applied to the sensitive
this hypothetically allows for greater range of motion to nociceptors can generate strong impulses, and these
decrease tension in these muscles.
impulses are transmitted to the spinal cord. It is likely
Recent evidence in understanding the pathophysiology of that these impulses can subsequently break the negative
MTrPs agree that local pain and tenderness at MTrPs may be cycle in which the neural circuit is responsible for the
intrinsic part of muscle ischemia associated with sustained MTrPs (the hypothetical “MTrP circuit”) in a manner
[38]
focal muscle contraction and/or muscle cramps. Massage similar to hyperstimulation analgesia. This is probably the
techniques seem to be more effective when applied to mechanism for remote pain control as described in this
superficial muscles than when applied to masseter muscles. study.
26 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 1 || Jun 2014