Page 24 - Read Online
P. 24
INTRODUCTION the dermis as it usually happens in nodulocystic acne;
however, it may also derive from the manipulation of
Acne is a chronic inflammatory disease of the less severe acne lesions by the patients themselves.
pilosebaceous unit, characterised by the presence of Two forms of scar are generally identified: hypertrophic
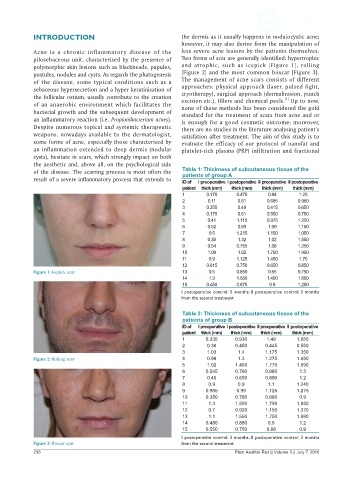
polymorphic skin lesions such as blackheads, papules, and atrophic, such as icepick [Figure 1], rolling
pustules, nodules and cysts. As regards the phatogenesis [Figure 2] and the most common boxcar [Figure 3].
of the disease, some typical conditions such as a The management of acne scars consists of different
sebaceous hypersecretion and a hyper keratinisation of approaches: physical approach (laser, pulsed light,
the follicular ostium, usually contribute to the creation cryotherapy), surgical approach (dermabrasion, punch
[1]
excision etc.), fillers and chemical peels. Up to now,
of an anaerobic environment which facilitates the none of these methods has been considered the gold
bacterial growth and the subsequent development of standard for the treatment of scars from acne and or
an inflammatory reaction (i.e. Propionibacterium acnes). is enough for a good cosmetic outcome; moreover,
Despite numerous topical and systemic therapeutic there are no studies in the literature analysing patient’s
weapons, nowadays available to the dermatologist, satisfation after treatment. The aim of this study is to
some forms of acne, especially those characterised by evaluate the efficacy of our protocol of nanofat and
an inflammation extended to deep dermis (nodular platelet-rich plasma (PRP) infiltration and fractional
cysts), hesitate in scars, which strongly impact on both
the aesthetic and, above all, on the psychological side
of the disease. The scarring process is most often the Table 1: Thickness of subcutaneous tissue of the
patients of group A
result of a severe inflammatory process that extends to ID of I preoperative I postoperative II preoperative II postoperative
patient thick (mm) thick (mm) thick (mm) thick (mm)
1 0.175 0.475 0.94 1.25
2 0.11 0.61 0.685 0.950
3 0.355 0.48 0.415 0.650
4 0.175 0.61 0.550 0.750
5 0.41 1.115 0.975 1.250
6 0.52 0.69 1.09 1.150
7 0.5 1.215 1.150 1.050
8 0.35 1.32 1.02 1.550
9 0.54 0.755 1.08 1.250
10 1.09 1.92 1.750 1.950
11 0.9 1.125 1.450 1.70
12 0.615 0.750 0.650 0.850
Figure 1: Icepick scar 13 0.5 0.650 0.55 0.750
14 1.3 1.550 1.450 1.650
15 0.450 0.875 0.9 1.250
I postoperative control: 3 months; II postoperative control: 3 months
from the second treatment
Table 2: Thickness of subcutaneous tissue of the
patients of group B
ID of I preoperative I postoperative II preoperative II postoperative
patient thick (mm) thick (mm) thick (mm) thick (mm)
1 0.335 0.930 1.48 1.650
2 0.36 0.450 0.445 0.550
3 1.03 1.4 1.175 1.350
Figure 2: Rolling scar 4 0.98 1.3 1.275 1.650
5 1.02 1.450 1.770 1.990
6 0.545 0.760 0.880 1.3
7 0.46 0.650 0.890 1.2
8 0.9 0.9 1.1 1.240
9 0.985 0.99 1.125 1.275
10 0.350 0.780 0.880 0.9
11 1.3 1.550 1.750 1.950
12 0.7 0.920 1.150 1.370
13 1.1 1.550 1.750 1.980
14 0.450 0.880 0.9 1.2
15 0.550 0.750 0.88 0.9
I postoperative control: 3 months; II postoperative control: 3 months
Figure 3: Boxcar scar from the second treatment
236 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || July 7, 2016