Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Figure 11: (a) Trachea wrapped with lateral thoracic artery flap, located
within the lateral thoraco-abdominal area; (b) two constructs can be
tunneled to two separate lateral neck incisions
Strap muscles and investing fascia are closed. Rabbits
do not tolerate foreign material such as a Penrose
drain to prevent possible air trapping. As a preventive
measure, loose, interrupted sutures are placed, taking
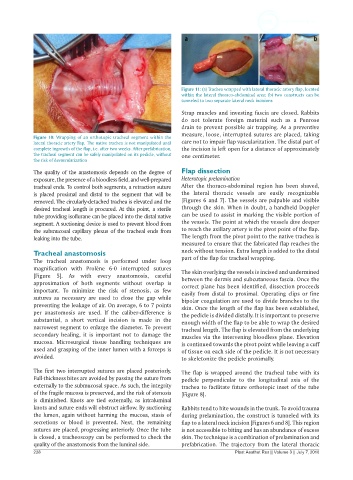
Figure 10: Wrapping of an orthotopic tracheal segment within the
lateral thoracic artery flap. The native trachea is not manipulated until care not to impair flap vascularization. The distal part of
complete ingrowth of the flap, i.e. after two weeks. After prefabrication, the incision is left open for a distance of approximately
the tracheal segment can be safely manipulated on its pedicle, without one centimeter.
the risk of devascularization
The quality of the anastomosis depends on the degree of Flap dissection
exposure, the presence of a bloodless field, and well-prepared Heterotopic prelamination
tracheal ends. To control both segments, a retraction suture After the thoraco-abdominal region has been shaved,
is placed proximal and distal to the segment that will be the lateral thoracic vessels are easily recognizable
removed. The circularly-detached trachea is elevated and the [Figures 6 and 7]. The vessels are palpable and visible
desired tracheal length is procured. At this point, a sterile through the skin. When in doubt, a handheld Doppler
tube providing isoflurane can be placed into the distal native can be used to assist in marking the visible portion of
segment. A suctioning device is used to prevent blood from the vessels. The point at which the vessels dive deeper
the submucosal capillary plexus of the tracheal ends from to reach the axillary artery is the pivot point of the flap.
leaking into the tube. The length from the pivot point to the native trachea is
measured to ensure that the fabricated flap reaches the
Tracheal anastomosis neck without tension. Extra length is added to the distal
The tracheal anastomosis is performed under loop part of the flap for tracheal wrapping.
magnification with Prolène 6-0 interrupted sutures The skin overlying the vessels is incised and undermined
[Figure 5]. As with every anastomosis, careful between the dermis and subcutaneous fascia. Once the
approximation of both segments without overlap is correct plane has been identified, dissection proceeds
important. To minimize the risk of stenosis, as few easily from distal to proximal. Operating clips or fine
sutures as necessary are used to close the gap while bipolar coagulation are used to divide branches to the
preventing the leakage of air. On average, 6 to 7 points skin. Once the length of the flap has been established,
per anastomosis are used. If the caliber-difference is the pedicle is divided distally. It is important to preserve
substantial, a short vertical incision is made in the enough width of the flap to be able to wrap the desired
narrowest segment to enlarge the diameter. To prevent tracheal length. The flap is elevated from the underlying
secondary healing, it is important not to damage the muscles via the intervening bloodless plane. Elevation
mucosa. Microsurgical tissue handling techniques are is continued towards the pivot point while leaving a cuff
used and grasping of the inner lumen with a forceps is of tissue on each side of the pedicle. It is not necessary
avoided. to skeletonize the pedicle proximally.
The first two interrupted sutures are placed posteriorly. The flap is wrapped around the tracheal tube with its
Full-thickness bites are avoided by passing the suture from pedicle perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the
externally to the submucosal space. As such, the integrity trachea to facilitate future orthotopic inset of the tube
of the fragile mucosa is preserved, and the risk of stenosis [Figure 8].
is diminished. Knots are tied externally, as intraluminal
knots and suture ends will obstruct airflow. By suctioning Rabbits tend to bite wounds in the trunk. To avoid trauma
the lumen, again without harming the mucosa, stasis of during prelamination, the construct is tunneled with its
secretions or blood is prevented. Next, the remaining flap to a lateral neck incision [Figures 6 and 8]. This region
sutures are placed, progressing anteriorly. Once the tube is not accessible to biting and has an abundance of excess
is closed, a tracheoscopy can be performed to check the skin. The technique is a combination of prelamination and
quality of the anastomosis from the luminal side. prefabrication. The trajectory from the lateral thoracic
228 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || July 7, 2016