Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
Figure 4: (a) Peroperative view on the pretracheal fascia with the
thyroid gland (green arrow), after dividing the strap muscles; (b) image
of posterior oesophageal branches (yellow arrow) after opening the
pretracheal fascia
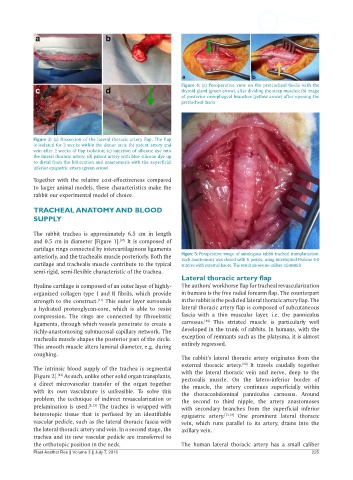
Figure 3: (a) Dissection of the lateral thoracic artery flap. The flap
is isolated for 2 weeks within the donor area; (b) patent artery and
vein after 2 weeks of flap isolation; (c) injection of silicone dye into
the lateral thoracic artery; (d) patent artery with blue silicone dye up
to distal from the bifurcation and anastomosis with the superficial
inferior epigastric artery (green arrow)
Together with the relative cost-effectiveness compared
to larger animal models, these characteristics make the
rabbit our experimental model of choice.
TRACHEAL ANATOMY AND BLOOD
SUPPLY
The rabbit trachea is approximately 6.5 cm in length
and 0.5 cm in diameter [Figure 1]. It is composed of
[10]
cartilage rings connected by intercartilaginous ligaments
anteriorly, and the trachealis muscle posteriorly. Both the Figure 5: Peroperative image of autologous rabbit tracheal transplantation.
Each anastomosis was closed with 6 points, using interrupted Prolène 6-0
cartilage and trachealis muscle contribute to the typical sutures with external knots. The result shows no caliber mismatch
semi-rigid, semi-flexible characteristic of the trachea.
Lateral thoracic artery flap
Hyaline cartilage is composed of an outer layer of highly- The authors’ workhorse flap for tracheal revascularization
organized collagen type I and II fibrils, which provide in humans is the free radial forearm flap. The counterpart
strength to the construct. This outer layer surrounds in the rabbit is the pedicled lateral thoracic artery flap. The
[11]
a hydrated proteoglycan-core, which is able to resist lateral thoracic artery flap is composed of subcutaneous
compression. The rings are connected by fibroelastic fascia with a thin muscular layer, i.e. the panniculus
[14]
ligaments, through which vessels penetrate to create a carnosus. This striated muscle is particularly well
richly-anastomosing submucosal capillary network. The developed in the trunk of rabbits. In humans, with the
trachealis muscle shapes the posterior part of the circle. exception of remnants such as the platysma, it is almost
This smooth muscle alters luminal diameter, e.g. during entirely regressed.
coughing.
The rabbit’s lateral thoracic artery originates from the
external thoracic artery. It travels caudally together
[14]
The intrinsic blood supply of the trachea is segmental with the lateral thoracic vein and nerve, deep to the
[Figure 2]. As such, unlike other solid organ transplants, pectoralis muscle. On the latero-inferior border of
[12]
a direct microvascular transfer of the organ together the muscle, the artery continues superficially within
with its own vasculature is unfeasible. To solve this the thoracoabdominal panniculus carnosus. Around
problem, the technique of indirect revascularization or the second to third nipple, the artery anastomoses
prelamination is used. [5,13] The trachea is wrapped with with secondary branches from the superficial inferior
heterotopic tissue that is perfused by an identifiable epigastric artery. [15,16] One prominent lateral thoracic
vascular pedicle, such as the lateral thoracic fascia with vein, which runs parallel to its artery, drains into the
the lateral thoracic artery and vein. In a second stage, the axillary vein.
trachea and its new vascular pedicle are transferred to
the orthotopic position in the neck. The human lateral thoracic artery has a small caliber
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || July 7, 2016 225