Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
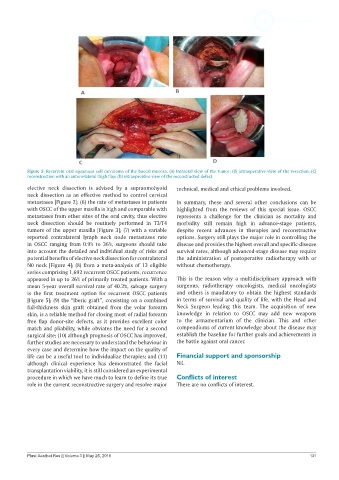
Figure 5: Recurrent oral squamous cell carcinoma of the buccal mucosa. (A) Intraoral view of the tumor; (B) intraoperative view of the resection; (C)
reconstruction with an antero-lateral thigh flap; (D) intraoperative view of the reconstructed defect
elective neck dissection is advised by a supraomohyoid technical, medical and ethical problems involved.
neck dissection as an effective method to control cervical
metastases [Figure 2]; (6) the rate of metastases in patients In summary, these and several other conclusions can be
with OSCC of the upper maxilla is high and comparable with highlighted from the reviews of this special issue. OSCC
metastases from other sites of the oral cavity, thus elective represents a challenge for the clinician as mortality and
neck dissection should be routinely performed in T3/T4 morbidity still remain high in advance-stage patients,
tumors of the upper maxilla [Figure 3]; (7) with a variable despite recent advances in therapies and reconstructive
reported contralateral lymph neck node metastases rate options. Surgery still plays the major role in controlling the
in OSCC ranging from 0.9% to 36%, surgeons should take disease and provides the highest overall and specific-disease
into account the detailed and individual study of risks and survival rates, although advanced-stage disease may require
potential benefits of elective neck dissection for contralateral the administration of postoperative radiotherapy with or
N0 neck [Figure 4]; (8) from a meta-analysis of 13 eligible without chemotherapy.
series comprising 1,692 recurrent OSCC patients, recurrence
appeared in up to 26% of primarily treated patients. With a This is the reason why a multidisciplinary approach with
mean 5-year overall survival rate of 40.2%, salvage surgery surgeons, radiotherapy oncologists, medical oncologists
is the first treatment option for recurrent OSCC patients and others is mandatory to obtain the highest standards
[Figure 5]; (9) the “Iberic graft”, consisting on a combined in terms of survival and quality of life, with the Head and
full-thickness skin graft obtained from the volar forearm Neck Surgeon leading this team. The acquisition of new
skin, is a reliable method for closing most of radial forearm knowledge in relation to OSCC may add new weapons
free flap donor-site defects, as it provides excellent color to the armamentarium of the clinician. This and other
match and pliability, while obviates the need for a second compendiums of current knowledge about the disease may
surgical site; (10) although prognosis of OSCC has improved, establish the baseline for further goals and achievements in
further studies are necessary to understand the behaviour in the battle against oral cancer.
every case and determine how the impact on the quality of
life can be a useful tool to individualize therapies; and (11) Financial support and sponsorship
although clinical experience has demonstrated the facial Nil.
transplantation viability, it is still considered an experimental
procedure in which we have much to learn to define its true Conflicts of interest
role in the current reconstructive surgery and resolve major There are no conflicts of interest.
Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016 131