Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
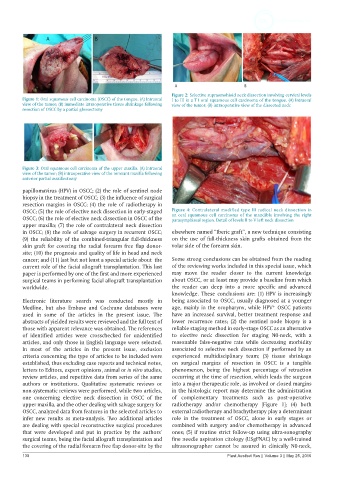
Figure 2: Selective supraomohioid neck dissection involving cervical levels
Figure 1: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) of the tongue. (A) Intraoral I to III in a T1 oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. (A) Intraoral
view of the tumor; (B) immediate intraoperative tissue shrinkage following view of the tumor; (B) intraoperative view of the dissected neck
resection of OSCC by a partial glossectomy
Figure 3: Oral squamous cell carcinoma of the upper maxilla. (A) Intraoral
view of the tumor; (B) intraoperative view of the remnant maxilla following
anterior partial maxillectomy
papillomavirus (HPV) in OSCC; (2) the role of sentinel node
biopsy in the treatment of OSCC; (3) the influence of surgical
resection margins in OSCC; (4) the role of radiotherapy in
OSCC; (5) the role of elective neck dissection in early-staged Figure 4: Contralateral modified type III radical neck dissection in
OSCC; (6) the role of elective neck dissection in OSCC of the an oral squamous cell carcinoma of the mandible involving the right
parasymphiseal region. Detail of levels II to V left neck dissection
upper maxilla; (7) the role of contralateral neck dissection
in OSCC; (8) the role of salvage surgery in recurrent OSCC; elsewhere named “Iberic graft”, a new technique consisting
(9) the reliability of the combined-triangular full-thickness on the use of full-thickness skin grafts obtained from the
skin graft for covering the radial forearm free flap donor- volar side of the forearm skin.
site; (10) the prognosis and quality of life in head and neck
cancer; and (11) last but not least a special article about the Some strong conclusions can be obtained from the reading
current role of the facial allograft transplantation. This last of the reviewing works included in this special issue, which
paper is performed by one of the first and more experienced may move the reader closer to the current knowledge
surgical teams in performing facial allograft transplantation about OSCC, or at least may provide a baseline from which
worldwide. the reader can deep into a more specific and advanced
knowledge. These conclusions are: (1) HPV is increasingly
Electronic literature search was conducted mostly in being associated to OSCC, usually diagnosed at a younger
Medline, but also Embase and Cochrane databases were age, mainly in the oropharynx, while HPV OSCC patients
+
used in some of the articles in the present issue. The have an increased survival, better treatment response and
abstracts of yielded results were reviewed and the full text of lower recurrence rates; (2) the sentinel node biopsy is a
those with apparent relevance was obtained. The references reliable staging method in early-stage OSCC as an alternative
of identified articles were crosschecked for unidentified to elective neck dissection for staging N0-neck, with a
articles, and only those in English language were selected. reasonable false-negative rate while decreasing morbidity
In most of the articles in the present issue, exclusion associated to selective neck dissection if performed by an
criteria concerning the type of articles to be included were experienced multidisciplinary team; (3) tissue shrinkage
established, thus excluding case reports and technical notes, on surgical margins of resection in OSCC is a tangible
letters to Editors, expert opinions, animal or in vitro studies, phenomenon, being the highest percentage of retraction
review articles, and repetitive data from series of the same occurring at the time of resection, which leads the surgeon
authors or institutions. Qualitative systematic reviews or into a major therapeutic role, as involved or closed margins
non-systematic reviews were performed, while two articles, in the histologic report may determine the administration
one concerning elective neck dissection in OSCC of the of complementary treatments such as post-operative
upper maxilla, and the other dealing with salvage surgery for radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy [Figure 1]; (4) both
OSCC, analyzed data from features in the selected articles to external radiotherapy and brachytherapy play a determinant
infer new results as meta-analysis. Two additional articles role in the treatment of OSCC, alone in early stages or
are dealing with special reconstructive surgical procedures combined with surgery and/or chemotherapy in advanced
that were developed and put in practice by the authors' ones; (5) if routine strict follow-up using ultra-sonography
surgical teams, being the facial allograft transplantation and fine needle aspiration citology (USgFNAC) by a well-trained
the covering of the radial forearm free flap donor-site by the ultrasonographer cannot be assured in clinically N0-neck,
130 Plast Aesthet Res || Volume 3 || May 25, 2016